Piperidine
Agent Name
Piperidine
Alternative Name
Hexahydropyridine
CAS Number
110-89-4
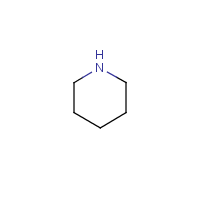
Formula
C5-H11-N
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
Hexahydropyridine; Azacyclohexane; Cyclopentimine; Cypentil; Hexazane; Pentamethyleneimine; Pentamethylenimine; Perhydropyridine; Piperidin [German]; Pyridine, hexahydro-; [ChemIDplus] UN2401
Category
Amines, Cyclic
Description
Colorless liquid with an amine odor; [HSDB]
Sources/Uses
Used as a chemical intermediate to produce drugs, wetting agents, and disinfectants; Also used as a rubber accelerator, a curing agent for epoxy resins, a flavoring agent, and an additive to oils and fuels; [HSDB]
Comments
Corrosive to skin; [Quick CPC] High inhalation exposure can cause pulmonary edema; [ICSC] Signs of toxicity in acute animal studies included respiratory distress, ataxia, weakness, paralysis, and convulsions; For humans, the irritation threshold is 26 ppm; workers can tolerate levels of 2-5 ppm for only a short period because of the odor; [AIHA] Oral doses of 30-60 mg/kg may cause weakness, vomiting, labored respiration, muscular paralysis, and asphyxia; [NTP] Safe when used as a flavoring agent in food; [JECFA] A skin sensitizer in guinea pigs; [EPA ChAMP] Causes impaired liver function tests in repeated dose inhalation studies of rats; [RTECS]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
32.1 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (mice) = 6,000 mg/m3/2hr
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold <2 ppm by volume; [AIHA] VP from HSDB;
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
WEEL
1 ppm
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: