Endrin
Agent Name
Endrin
CAS Number
72-20-8
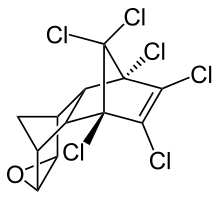
Formula
C12-H8-Cl6-O
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
1,2,3,4,10,10-Hexachloro-6,7-epoxy-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,4-endo,endo-5,8-dimethanonaphthalene; Hexadrin; [NIOSH]
Category
Organochlorine Pesticides
Description
Colorless to tan, crystalline solid with a mild, chemical odor. [insecticide]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Formerly used as an insecticide, as an avicide, and as a rodenticide; [HSDB]
Comments
High-dose animal studies show that organochlorine insecticides can cause liver injury. [LaDou, p. 593] "No evidence of hepatic injury in humans as the result of environmental contamination." [Zimmerman, p. 414]
Restricted
Voluntary cancellation in 1985; all U.S. registrations cancelled; [EPA Pesticides, p. 56]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
Bioaccumulates
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
0.1 mg/m3
MAK
0.05 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
IDLH (NIOSH)
2 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: An oral dose of 171 mg/kg has been reported to be lethal [Runhaar et al. 1985]. It has also been reported that the approximate oral dose producing convulsions is about 0.2 mg/kg [Hayes 1982]. [Note: Oral doses of 171 mg/kg or 0.2 mg/kg are equivalent to a 70kg worker being exposed to about 8,000 mg/m3 or 9 mg/m3, respectively, for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
3E-06 mm Hg
Half Life
No reports found; [TDR, p. 613]
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Other Poison
Organochlorine
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: