4,4'-Methylenedianiline
Agent Name
4,4'-Methylenedianiline
Alternative Name
MDA
CAS Number
101-77-9
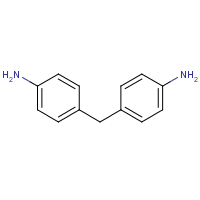
Formula
C13-H14-N2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
4,4'-Methylenedianiline; 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethan [German]; 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane; 4,4'-Dimethylenediamine; 4,4'-Diphenylmethanediamine; 4,4'-Methylenebis(benzeneamine); 4,4'-Methylenebisaniline; 4,4'-Methylenedianiline; 4-(4-Aminobenzyl)aniline; Ancamine TL; Aniline, 4,4'-methylenedi-; Araldite hardener 972; Avaldite HT 972; Benzenamine, 4,4'-methylenebis-; Bis(4-aminophenyl)methane; Bis(p-aminophenyl)methane; Bis-p-aminofenylmethan [Czech]; Curithane; Dadpm; Di-(4-aminophenyl)methane; Diaminodiphenylmethane; Dianilinemethane; Dianilinomethane; Epicure DDM; Epikure DDM; HT 972; Jeffamine AP-20; MDA; Methylenebis(aniline); Methylenedianiline; Methylenedianiline (VAN); Sumicure M; Tonox; p,p'-Diaminodifenylmethan [Czech]; p,p'-Diaminodiphenylmethane; p,p'-Methylenedianiline; p-Toluidine, alpha-(p-aminophenyl)-; [ChemIDplus] UN2651
Category
Amines, Polyaromatic
Description
Pale-brown, crystalline solid with a faint, amine-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a chemical intermediate, lab analytic agent, and monomer for polyamide and polymide resins; [HSDB] Used primarily in the manufacture of rubber and plastics; used as an epoxy resin hardener in the following applications: glues, paints, inks, polyvinylchloride products, dental bonding agents, and microelectronic encapsulations; [Marks, p. 269]
Comments
Has caused liver injury after occupational exposure; "Some of the most commonly used curing agents in the advanced composite industry are the aromatic amines. Two of the most common are 4,4'-methylene-dianiline (MDA) and 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (DDS). Like the epoxies, these compounds have a very low vapor pressure and usually do not present an airborne hazard unless in a mixture that is sprayed or cured at high temperatures. However, potential for dermal exposure is frequently high. The aromatic amines may permeate many of the commonly used protective gloves and thus may be particularly difficult to protect against." [OSHA Technical Manual: Advanced Composites] A rare cause of occupational allergic contact dermatitis; [Marks, p. 268-70] Merck Index #2980; A potential skin sensitizer and liver toxicant; [ICSC]
Restricted
Carcinogen--See 29 CFR 1910.1050
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
0.01 ppm, STEL(OSHA) = 0.1 ppm
Vapor Pressure
2E-07 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 220 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Plasma: 13 hours; urine: 7 hours; [TDR, p. 872]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
must be preheated
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Hepatotoxin
Occupational hepatotoxin (principal effect)
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: