alpha-Amanitin
Agent Name
alpha-Amanitin
CAS Number
23109-05-9
Formula
C39-H54-N10-O14-S
Major Category
Biological Agents
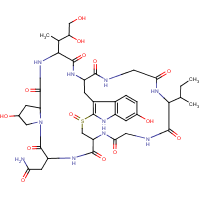
Synonyms
Cyclic(L-asparaginyl-4-hydroxy-L-prolyl-(R)-4,5-dihydroxy-L-isoleucyl-6-hydroxy-2-mercapto-L-tryptophylglycyl-L-isoleucylglycyl-L-cysteinyl), cyclic (4-8)-sulfide, (R)-S-oxide; alpha-Amanitine; alpha-Amatoxin; [ChemIDplus] UN3462
Category
Mushroom Toxins
Description
Solid; [Merck Index] Faintly beige powder; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
A toxin from the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides; Used in molecular biology research; [Merck Index]
Comments
Inhibits protein synthesis in mammalian cells; Generally no symptoms for 6 to 15 hours after ingestion; Symptoms of poisoned patients include severe gastroenteritis, hyperglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, liver necrosis, renal failure, and death; [Merck Index] Emergency treatment: "Mushrooms- cyclopeptides"; [HSDB] 95% of deaths caused by mushroom poisoning are caused by amatoxins produced by the Amanita and Gyromitra species. The amatoxins cause a delayed gastroenteritis at least 4-8 hours after ingestion, often followed by liver and kidney failure 24-48 hours after ingestion of the poisonous mushrooms. The diarrhea is typically watery or "cholera-like" and may be profuse enough to cause dehydration and shock. Of 10,584 mushroom exposures reported by the American Association of Poison Control Centers in 1996, only 54 were due to the potentially fatal amatoxins. The most common illness following mushroom ingestion is a self-limited gastroenteritis after a short latency of less than 2 hours. Some mushrooms contain neurological toxins such as the hallucinogenic psilocybin or the cholinergic muscarine. Mushroom neurotoxins also have a short latency, usually 15-30 minutes. [Ford, p. 899-908; Foodborne Illnesses. MMWR. 4/16/04; See "beta-Amanitin."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Explanatory Notes
The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Toxins, extracted from living sources, solid, n.o.s."
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Other Information
No other related information on this agent was found.