Diethylene glycol
Agent Name
Diethylene glycol
Alternative Name
DEG
CAS Number
111-46-6
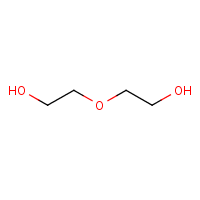
Formula
C4-H10-O3
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
1,5-Dihydroxy-3-oxapentane; 2,2'-0xydiethanol; 2,2'-Dihydroxydiethyl ether; 2,2'-Dihydroxyethyl ether; 2,2'-Oxybisethanol; 2,2'-Oxydiethanol; 2,2'-Oxyethanol; 2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)ethanol; 3-Oxapentamethylene-1,5-diol; 3-Oxapentane-1,5-diol; Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ether; Bis(beta-hydroxyethyl) ether; Brecolane NDG; DEG; Deactivator E; Dicol; Diethylenglykol [Czech]; Digenos; Diglycol; Digol; Dihydroxydiethyl ether; Dissolvant APV; Ethanol, 2,2'-oxybis-; Ethanol, 2,2'-oxydi-; Ethylene diglycol; Glycol ether; Glycol ethyl ether; TL4N; beta,beta'-Dihydroxydiethyl ether; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Ethylene Glycols
Description
Very hygroscopic, colorless liquid; [Hawley]
Sources/Uses
Used as a humectant (tobacco, casein, synthetic sponges, composition corks, glues, gelatin, and paper products), a dehydrating agent (plasticizers, surfactants, and natural gas), a lubricating and finishing agent (wool, worsted, cotton, rayon, and silk), a solvent for vat dyes, an intermediate (triethylene glycol and diethylene glycol dinitrate), a petroleum extraction solvent, and a monomer (unsaturated polyester resins and polyols for polyurethane); Also used in lacquers, cosmetics, antifreeze solutions for sprinkler systems; water seals for gas tanks, brake fluids, lubricants, mold release agents, and inks; [HSDB] Used mainly to produce unsaturated polyester resins, polyols, and polyurethanes; [Reference #1]
Comments
Repeated oral doses in animal experiments causes renal injury; Low toxicity by the dermal route; No evidence of carcinogenicity in animals; [Reference #1] Toxic by ingestion--may cause damage to the liver, kidneys, and CNS; [ICSC] A mild irritant based on animal studies; Targets the liver, kidneys, and CNS; [MSDSonline] In 1937, 96 deaths were attributed to ingestion of "elixir of sulphanilamide" that contained 72% DEG; Deaths occurred about 9 days after ingestion with vomiting, acute renal failure, convulsions, and coma. Autopsies showed severe kidney and liver damage. [AIHA] See "GLYCOL ETHERS."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
MAK
44 mg/m3
Vapor Pressure
0.0057 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) > 4,600 mg/m3/4h
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 124 deg C; [ICSC] VP from ChemIDplus;
NFPA
must be preheated
WEEL
10 mg/m3
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: