Triorthocresyl phosphate
Agent Name
Triorthocresyl phosphate
CAS Number
78-30-8
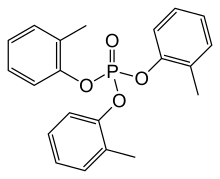
Formula
C21-H21-O4-P
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
TCP; TOCP; Tri-o-cresyl phosphate; Tri-o-cresyl ester of phosphoric acid; [NIOSH]
Category
Organophosphates, Other
Description
Colorless to pale-yellow, odorless liquid or solid (below 52 degrees F). [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a flame retardant, plasticizer, lubricant, additive to gasoline and hydraulic fluids, and intermediate for pharmaceuticals. Also used in coatings and adhesives, in adhesives for air filter media, as a heat exchange medium, a waterproofing agent, an extraction solvent, and in solvent mixtures for resins; [ACGIH]
Comments
Ingested TOCP was the cause of "ginger jake paralysis" or "jake leg," a form of organophosphate induced delayed neuropathy (OPIDN). The minimum paralytic dose in humans by ingestion is approximately 10 to 30 mg/kg. Reported adverse effects after occupational exposure include reduced plasma cholinesterase activity and peripheral neuropathy. No neurological abnormalities were found after careful examination of workers exposed over several months to hydraulic fluid containing 21% TOCP and air concentrations of 1.5 mg/m3. Toxicity depends on the concentration of ortho-configured components. "It should be noted that TOCP does not produce typical symptoms such as those associated with acetylcholinesterase inhibition like those seen with phosphate esters such as parathion." [ACGIH] See "Tricresyl phosphate (mixed isomers," "Tri-m-cresyl phosphate," and "Tri-p-cresyl phosphate."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Acetylcholinesterase activity in red blood cells = 70% of individual's baseline; Butylcholinesterase activity in serum or plasma = 60% of individual's baseline; Sample at end of shift; [TLVs and BEIs]
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.02 mg/m3, inhalable fraction and vapor
PEL (OSHA)
0.1 mg/m3
IDLH (NIOSH)
40 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: It has been reported that serious paralysis has been produced by an oral dose of about 6.6 mg/kg [Deichmann and Gerarde 1969] and that the probable lethal dose is greater than 28 mg/kg [Patty 1963]. [Note: Oral doses of 6.5 or 28 mg/kg are equivalent to a 70kg worker being exposed to about 300 or 1,300 mg/m3, respectively, for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
2E-05 mm Hg
NFPA
must be preheated
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Predominantly motor
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Other Information
No other related information on this agent was found.