o-Nitrochlorobenzene
Agent Name
o-Nitrochlorobenzene
Alternative Name
o-Chloronitrobenzene
CAS Number
88-73-3
Formula
C6-H4-Cl-N-O2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
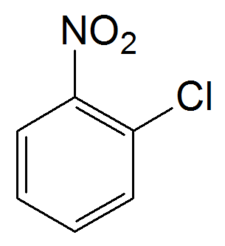
Synonyms
1-Chloro-2-nitrobenzene; 1-Nitro-2-chlorobenzene; 2-Chloro-1-nitrobenzene; 2-Chloronitrobenzene; 2-Nitrochlorobenzene; ONCB; o-Chloronitrobenzene; o-Nitrochlorobenzene; [ChemIDplus] UN1578
Category
Nitros, Aromatic
Description
Yellow crystals with an aromatic odor; [CAMEO]
Sources/Uses
"Used as an intermediate in the manufacture of o-aminophenol (used as a developer in the photography industry); [HDSB]
Comments
Crystals may cause severe skin burns. [HSDB] Listed in a table of "Industrial Chemicals for Which Methemoglobin Formation is the Principal Cause of Toxicity"; [ACGIH] "In the United Kingdom between 1961 and 1980, chloroaniline, p-toluidine, nitrobenzene, and nitrochlorobenzene were the most common industrial causes of methemoglobinemia. Dermal exposure was a more frequent route of toxicity than inhalation with these compounds." (Ellenhorn, M.J. and D.G. Barceloux. Medical Toxicology - Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Poisoning. New York, NY: Elsevier Science Publishing Co., Inc. 1988.) Can cause methemoglobinemia after acute exposure and anemia and liver damage after chronic exposure; [ICSC]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Methemoglobin in blood = 1.5% of hemoglobin during or end of shift
Vapor Pressure
0.018 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 3,200 mg/m3/4h
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 127 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Adverse Effects
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is primary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: