2,4-Dinitrotoluene
Agent Name
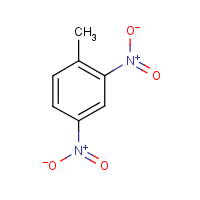
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
CAS Number
121-14-2
Formula
C7-H6-N2-O4
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1-Methyl-2,4-dinitrobenzene; 2,4-DNT; 2,4-Dinitro-1-methylbenzene; 2,4-Dinitromethylbenzene; 2,4-Dinitrotoluene; 2,4-Dinitrotoluol; 4-Methyl-1,3-dinitrobenzene; Toluene, 2,4-dinitro-; Benzene, 1-methyl-2,4-dinitro-; [ChemIDplus] UN3454; UN1600 (molten)
Category
Nitros, Aromatic
Description
Yellow solid; [ICSC] Yellow to red solid; Yellow liquid when heated; [CHRIS]
Sources/Uses
Used to make dyes, explosives, munitions, propellants, rubber chemicals, plastics, and other chemicals; [HSDB] The technical grade (approximately 80/20 of the 2,4/2,6 isomers) is used primarily as an intermediate for toluene diamines and diisocyanates; [IARC]
Comments
Can induce methemoglobinemia; Can be absorbed through skin; [ICSC] A mucous membrane irritant; May cause methemoglobinemia; [HSDB] Allergic contact dermatitis reported in a worker manufacturing explosives and exposed to 2,4-dinitrotoluene and nitroglycerin; [Kanerva, p. 1788] Chronic exposure may cause liver injury, anemia, and neuritis; [CHRIS] Equivocal evidence for human reproductive toxicity; [ToxPlanet: DOE] No evidence of teratogenicity in rats or mice at doses maternally toxic; A decrease in sperm positive females was observed in a study of rats when males were dosed at 240 mg/kg/day; [REPROTOX] See "Dinitrotoluene, all isomers."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
0.000147 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Dinitrotoluenes, solid." VP from ChemIDplus;
NFPA
must be preheated
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: