Octane
Agent Name
Octane
CAS Number
111-65-9
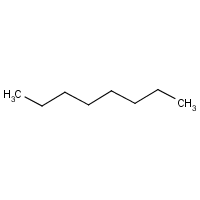
Formula
C8-H18
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
n-Octane; normal-Octane; [NIOSH] Oktan [Polish]; Oktanen [Dutch]; Ottani [Italian]; [ChemIDplus] UN1262
Category
Aliphatics, Saturated (<C12)
Description
Colorless liquid with a gasoline-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent, chemical raw material, antiknock agent for high compression engine fuels, lacquer diluent, carrier solvent in polymer manufacturing, blowing agent for foam rubber used in rocket propellants, for calibrations, and azeotropic distillations; [HSDB]
Comments
A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; Ingestion can cause aspiration into the lungs; Inhalation may cause lowering of consciousness; [ICSC] Inhalation of vapor may cause giddiness, vertigo, headache, anesthetic stupor, and convulsions; Five hour dermal exposure causes blisters but no anesthesia; [HSDB] A skin irritant; Inhalation may cause drowsiness or dizziness; An aspiration hazard by ingestion (may cause lung injury); [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
300 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
500 ppm
MAK
500 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
1000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: The narcotic concentration has been estimated to be either 8,000 ppm [Flury and Zernik 1931] or 10,000 ppm [Patty and Yant 1929]. The fatal concentration has been estimated to be 13,500 ppm [Flury and Zernik 1931].
Vapor Pressure
14.1 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
15 ppm
Odor Threshold High
235 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 118,000 mg/m3/4hr
Explanatory Notes
IDLH = 10% LEL (lower explosive limit); Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 150 ppm); TLV and PEL for all isomers of octane; MAK for all except Trimethylpentane isomers; [Guide to Occupational Exposure Values] VP from HSDB;
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: