1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
Agent Name
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
CAS Number
79-34-5
Formula
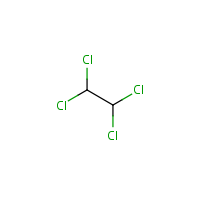
C2-H2-Cl4
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Tetrachloroethane, 1,1,2,2-; 1,1,2,2-Czterochloroetan [Polish]; 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloorethaan [Dutch]; 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloraethan [German]; 1,1,2,2-Tetrachlorethane [French]; 1,1,2,2-Tetracloroetano [Italian]; 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-dichloroethane; Acetosal; Acetylene tetrachloride; Bonoform; Cellon; Dichloro-2,2-dichloroethane; Ethane, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro-; s-Tetrachloroethane; TCE (ambiguous); Tetrachlorethane; Tetrachloroethane; Tetrachloroethane (VAN); Tetrachlorure d'acetylene [French]; Westron; [ChemIDplus] Boroform; F 130; F 130 (halocarbon); sym-Tetrachloroethane; Symmetrical tetrachloroethane; TCA; TCE; 1,1,2,2-TCE; [CAMEO] UN1702
Category
Chlorinated Aliphatics
Description
Colorless to pale-yellow liquid with a pungent, chloroform-like odor; [NIOSH] Heavy liquid with a sweetish suffocating odor like chloroform; [Merck Index] Clear colorless liquid; [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used in synthesis of organic chemicals; used in the past as a solvent for degreasing and extracting; [ACGIH] Used as a nonflammable solvent for fats, oils, waxes, resins, cellulose acetate, rubber, copal, phosphorus, and sulfur, as a solvent in certain types of Friedel-Crafts reactions or phthalic anhydride condensations, to make paints, varnishes, rust removers, trichloroethylene, and other chlorinated hydrocarbons with two carbon atoms, in soil sterilization, weed killer, and insecticide formulations, in the determination of theobromine in cacao, as immersion fluid in crystallography, and to produce pathological changes in gastrointestinal tract, liver, and kidneys in the laboratory; [Merck Index] Other uses include alcohol denaturant, fumigant, dry cleaning agent, in photographic film, cement, and to make artificial silk, leather, and pearls; [NTP] Currently only produced and consumed on site in closed systems for the synthesis of other chlorinated hydrocarbons; [Reference #1]
Comments
Many cases of occupational toxic hepatitis were reported in the past. [ACGIH] At high enough concentrations, can induce lacrimation, narcosis, and liver damage; [CAMEO] A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; May cause CNS depression and impaired function; May cause kidney and liver injury; Can be absorbed through skin; [ICSC] No evidence of carcinogenicity in mice or rats; [NTP] Highly toxic to humans by acute exposure, mainly targeting the liver and kidney; May also cause nervous system and hematological system injury; Lack of data and conflicting results do not allow for assessment of reproductive or developmental toxicity; [Reference #1] May cause irritation; Toxic by ingestion; Highly toxic by inhalation and skin absorption; Targets the nerves, liver, and blood; [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS]
Restricted
Not found in any pesticide products registered in the US; [NPIRS]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
1 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
5 ppm
MAK
1 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
100 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: A 30minute exposure to 146 ppm has caused vertigo, irritation of the mucous membranes, sense of pressure in the head, and fatigue; the same effects were noted after a 10minute exposure to 335 ppm [Lehmann et al. 1936; Negherbon 1959].
Vapor Pressure
5.74 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.23 ppm
Odor Threshold High
7.9 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 1,000 ppm/4hr
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 7.3 ppm); VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Lachrymator
Yes
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Occupational hepatotoxin (principal effect)
Nephrotoxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: