Aramid fibers
Agent Name
Aramid fibers
CAS Number
24938-64-5
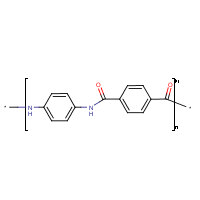
Formula
(C14-H10-N2-O2)mult-
Major Category
Plastics & Rubber
Synonyms
Aramica; Aramid fibers; Aramika; Kevlar 149; Kevlar 29; Kevlar 49; Poly(imino-p-phenyleneiminoterephthaloyl); Poly(p-phenylene terephthalamide); Kevlar 49; Poly(imino-1,4-phenyleneiminocarbonyl-1,4-phenylenecarbonyl); [ChemIDplus]
Category
Plastic & Rubber Dusts/Fumes
Sources/Uses
Chemical and fire resistant, high strength synthetic fiber used to make advanced composite materials; derived from p-phenylenediamine and terephthaloyl chloride; [Hawley] Used to reinforce composite materials for aerospace and sports equipment and to make woven protective apparel and automotive brake pads and gaskets; [IARC] Introduced by DuPont in the early 1970s under the trademark Kevlar, a condensation product of p-phenylenediamine and terephthalic acid; Other aramid fibers are Enka from the Netherlands and Teijin from Japan; Used in tires, ropes, cables, ballistic protection, coated fabrics, tapes, friction products, gaskets, and reinforced plastics; [Ullmann]
Comments
Highest occupational exposures produced during processing of shorter fibers in yarn; Rats exposed for 2 years to para-aramid fibrils have minimal pulmonary fibrosis; Studies in rats show that the fibrils are biodegradable in the lungs; Rats had increased incidence of pulmonary keratinizing cysts; "The biological significance of these lesions is unclear." [IARC]
Biomedical References
Adverse Effects
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: