2-Butoxyethanol
Agent Name
2-Butoxyethanol
Alternative Name
EGBE
CAS Number
111-76-2
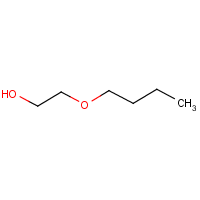
Formula
C6-H14-O2
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Ethylene glycol monobutyl ether; 2-Butoxy-1-ethanol; 2-Butoxyethanol; 3-Oxa-1-heptanol; BUCS; Butoxyethanol; Butyl cellosolve; Butyl cellu-sol; Butyl glycol; Butyl oxitol; Chimec NR; Dowanol EB; EGBE; EGMBE; Ektasolve EB; Ethanol, 2-butoxy-; Ethylene glycol butyl ether; Ethylene glycol n-butyl ether; Ethylene glycol, monobutyl ether; Gafcol EB; Glycol butyl ether; Glycol ether EB; Glycol monobutyl ether; Jeffersol EB; Monobutyl ether of ethylene glycol; Monobutyl ethylene glycol ether; O-Butyl ethylene glycol; Poly-Solv EB; n-Butoxyethanol; [ChemIDplus] UN2369
Category
Glycol Ethers (E Series)
Description
Colorless liquid with a mild, ether-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as solvent in surface coatings; [ACGIH] Also used in hydraulic fluids, glass cleaners, and leather cleaners; [Sullivan, p. 1203] Used as a solvent in paints, coatings, inks, metal cleaners, and household cleaners; Occupational exposures are high in silk screen printing; [Reference #2]
Comments
Severe hemoglobinuria and changes in the lungs, kidneys, and liver are seen in mice after 7-hour lethal concentration studies. Volunteers showed no evidence of adverse effects other than mucous membrane irritation after 8 hour exposures to 200 ppm. No increase in red cell fragility was seen after these brief exposures. [ACGIH] For ethylene glycol ethers, there is limited positive evidence of spontaneous abortions and decreased sperm counts in humans and strong positive evidence of birth defects and testicular damage in animals. [ATSDR Case Studies # 29] Humans are resistant to butoxyethanol-induced red blood cell hemolysis. [Sullivan, p. 1204] See "Glycol ethers."
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Butoxyacetic acid (BAA) in urine (with hydrolysis) = 200 mg/g creatinine at end of shift.
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
No
TLV (ACGIH)
20 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
50 ppm
MAK
10 ppm, sum of the concentrations of EGBE and its acetate in air
IDLH (NIOSH)
700 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: It has been stated that humans would be able to tolerate saturated concentrations (i.e., about 1,000 ppm) for 1 hour without experiencing any significant nonreversible effects [Carpenter et al. 1956].
Vapor Pressure
0.88 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.1 ppm
Odor Threshold High
0.35 ppm
RD50
2824 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat)= 450 ppm/4hr;
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.1 ppm); Flash point = 62 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Half Life
0.6 to 4.8 hours [Sullivan, p. 1203]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure:
Activities
Activities with risk of exposure: