2-Methoxyethanol
Agent Name
2-Methoxyethanol
Alternative Name
EGME
CAS Number
109-86-4
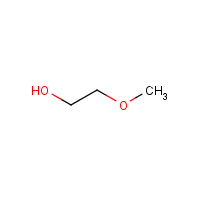
Formula
C3-H8-O2
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; 1-Hydroxy-2-methoxyethane; 2-Methoxy-1-ethanol; 2-Methoxy-aethanol [German]; 2-Methoxyethyl alcohol; 2-Metossietanolo [Italian]; 3-Oxa-1-butanol; Aethylenglykol-monomethylaether [German]; Amsco-Solv EE; Dowanol 7; Dowanol EM; EGME; Ethanol, 2-methoxy-; Ether monomethylique de l'ethylene-glycol [French]; Ethylene glycol methyl ether; Ethylene glycol monomethyl ether; Ethyleneglycol monomethyl ether; Glycol ether EM; Glycol monomethyl ether; Jeffersol EM; MECS; Methoxyhydroxyethane; Methyl cellosolve; Methyl glycol; Methyl oxitol; Methylcelosolv [Czech]; Methylglykol [German]; Metil cellosolve [Italian]; Metoksyetylowy alkohol [Polish]; Monoethylene glycol methyl ether; Monomethyl ether of ethylene glycol; Monomethyl glycol; Poly-Solv EM; Prist; [ChemIDplus] UN1188
Category
Glycol Ethers (E Series)
Description
Colorless liquid with a mild, ether-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent for many different purposes, (e.g., varnishes, dyes, and resins) and as a jet deicing additive; [ACGIH] Used in the Asian microelectronics industry in photoresist formulations and in manufacturing copper-laminate circuit boards; [JOEM 2004;46:707-713]
Comments
EGME is toxic to the bone marrow and testicles. Workers exposed to high levels are at risk for granulocytopenia, macrocytic anemia, oligospermia, and azoospermia. A study of shipyard painters with evidence of testicular toxicity showed EGME TWA concentrations of up to 5.7 ppm (mean = 0.83 ppm) along with 2-ethoxyethanol TWA exposures at up to 22 ppm. Because EGME is readily absorbed through the skin, air levels are an inadequate assessment of exposure. In lethal concentration studies in rats, death is due to lung and kidney damage. Liver injury is observed in animals after subchronic inhalation studies. [ACGIH] CNS depression has not been seen after acute occupational exposure, but there have been reports of encephalopathy in workers exposed to 2-methoxyethanol over a period of weeks to months. [LaDou, p. 549] For ethylene glycol ethers, there is limited positive evidence of spontaneous abortions and decreased sperm counts in humans and strong positive evidence of birth defects and testicular damage in animals. [ATSDR Case Studies # 29] 53 workers exposed to EGME manufacturing copper-laminate circuit boards in Taiwan did not have evidence of liver toxicity compared to the control group. [Loh CH, et al. Hepatic Effects in Workers Exposed to 2-Methoxy Ethanol. J Occup Environ Med 2004;46:707-713] Potential adverse effects include injury to the bone marrow, liver, kidneys, and CNS (unconsciousness). May be a reproductive toxin, cause anemia, and defat the skin; [ICSC] In animal experiments, causes congenital malformations and injury to the testes; Evidence of reproductive effects in humans has not been convincing; [REPROTOX] Labeled as "May impair fertility" and "May cause harm to the unborn child" by EU regulations; [Glycol Ethers Online]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
2-Methoxyacetic acid in urine = 1 mg/g creatinine; end of shift at end of workweek; [ACGIH]
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
25 ppm
MAK
1 ppm, sum of concentrations of CAS 109-86-4 and its acetate in air
IDLH (NIOSH)
200 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: Based on a UCC [1969] report that 0 of 6 rats died after a 2hour exposure to 2,000 ppm, 4 of 6 rats died after a 4hour exposure to 2,000 ppm, and 6 of 6 rats died after an 8hour exposure to 2,000 ppm, an IDLH of 2,000 ppm was chosen. . . . Human data: Chronic exposure to 50 to 100 ppm has been associated with headache, dizziness, lethargy, weakness, hyperreflexia, disorientation, unequal pupil size, and visual and/or auditory disturbances [ACGIH 1991]. It has been reported that 3,380 mg/kg is the lethal oral dose [Young and Woolner 1946]. [Note: An oral dose of 3,380 mg/kg is equivalent to a 70kg worker being exposed to about 50,000 ppm for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
9.5 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.09 ppm
Odor Threshold High
61 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 1,500 ppm/7H
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 2.4 ppm); Flash point = 41.7 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Aplastic anemia
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: