Quinidine
Agent Name
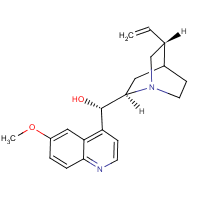
Quinidine
CAS Number
56-54-2
Formula
C20-H24-N2-O2
Major Category
Biological Agents
Synonyms
(+)-Quinidine; (8R,9S)-Quinidine; (9S)-6'-Methoxycinchonan-9-ol; (9S)-6-Methoxy-alpha-(5-vinyl-2-quinuclidinyl)-4-quinolinemethanol; Chinidin [German]; Cinchonan-9-ol, 6'-methoxy-, (9S)-; Conchinin; Conquinine; Pitayine; alpha-(6-Methoxy-4-quinolyl)-5-vinyl-2-quinuclidinemethanol (9S)-; beta-Quinine; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Plant Toxins
Description
Triboluminescent solid; [Merck Index]
Sources/Uses
Used as a human and veterinary antiarrhythmic and human antimalarial; [Merck Index]
Comments
"Quinidine sulfate has elicited contact allergy in production workers, and patch test with quinine were negative." [Kanerva, p. 435] Quinidine may induce photosensitivity in patients taking it systemically (photodrug reaction). [Marks, p. 201-3] As an oral medication, quinidine is used to treat heart arrhythmias. Many side effects have been reported after ingestion of therapeutic doses, including immune hemolytic anemia and drug-induced hepatitis. [HSDB] Therapeutic serum levels are 2-4 mg/L, and serious adverse effects are unusual in that range. A one gram dose is potentially lethal to adults. Toxic effects include ventricular tachycardia and depression of cardiac contractility. Other symptoms are vomiting, diarrhea, and anticholinergic effects. Seizures and coma may follow. Symptoms of chronic poisoning (cinchonism) are tinnitus, vertigo, deafness, and visual disturbances. [Olson, p. 398-9]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: