Tetramethyl lead
Agent Name
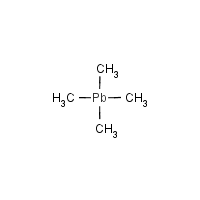
Tetramethyl lead
CAS Number
75-74-1
Formula
C4-H12-Pb
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Lead tetramethyl; Tetramethylplumbane; TML; [NIOSH]
Category
Metals, Organic Compounds
Description
Colorless liquid (unless dyed red, orange, or blue) with a fruity odor. [Note: Main usage is in anti-knock additives for gasoline.] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Tetraethyl and tetramethyl lead (CAS # 78-00-2 & 75-74-1), also called alkyl lead, are used as anti-knock agents in gasoline. [ATSDR Case Studies # 1]
Comments
The presenting symptoms of acute alkyl lead intoxication are anorexia, insomnia, fatigue, weakness, headache, depression, and irritability. [ATSDR Case Studies # 1] Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, or skin absorption. Overexposure may cause disturbed vision, tremors, seizures, and brain damage. Monitor workers with urinary lead measurements. [ACGIH] Lead compounds, organic, are not classifiable as to carcinogenicity to humans. [IARC] See "Lead" and linked occupational diseases.
Restricted
Organic lead was added to gasoline in the US until January 1996. [ATSDR Case Studies, Lead Toxicity]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
Bioaccumulates
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.15 mg/m3, as Pb
PEL (OSHA)
0.075 mg/m3, as Pb
MAK
0.004 mg/m3, as Pb
IDLH (NIOSH)
40 mg/m3, as Pb
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other animal data: It has been reported that signs of acute tetramethyl lead intoxication in rats were similar to that seen after acute poisoning with tetraethyl lead [ACGIH 1991].
Vapor Pressure
26 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (mice) = 8,500 mg/m3/30M
Explanatory Notes
VP from HSDB;
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: