Chlorodiethylaluminum
Agent Name
Chlorodiethylaluminum
CAS Number
96-10-6
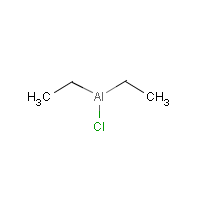
Formula
C4-H10-Al-Cl
Major Category
Metals
Synonyms
Aluminum diethyl monochloride; Aluminum, chlorodiethyl-; Aluminum, dichlorotetraethyldi-; DEAK; Deac; Diethylaluminium chloride; Diethylaluminum monochloride; Diethylchloroaluminum; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Metals, Organic Compounds
Description
Colorless liquid (will ignite spontaneously in air); [Hawley]
Sources/Uses
Used as a catalyst for thermoplastic polymers and an intermediate for organometallic compounds; [Hawley] Used as military incendiary agent; [Sullivan, p. 979] Organic aluminum compounds are "some of the most important, highest volume, highest value organometallic compounds in production." [Ullmann]
Comments
Aluminum alkyl halides release large amounts of HCl when spilled in water; [ERG 2016] Reacts violently with water and air; Decomposition products include flammable vapors, HCl, AlCl3, and aluminum containing dust; Causes thermal burns to skin and eyes; Inhalation can cause pulmonary edema; [CHEMINFO MSDS] Organoaluminum compounds are corrosive; Harmful if absorbed through the skin or inhaled; The butyl alkyls and below are pyrophoric; Aluminum alkyls are eye irritants; [HSDB] Organic aluminum compounds can cause irritation or burns, depending upon concentration; [Ullmann] TLV withdrawn for aluminum alkyls because of inadequate toxicological data; [ACGIH] See "Aluminum." See "ORGANOMETALS."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TIH
Yes
Dangerous When Wet
Yes
Vapor Pressure
0.17 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 11,000 mg/m3
Explanatory Notes
TLV withdrawn in 2008 with adoption of "Aluminum metal and insoluble compounds"; TLV not recommended for soluble nor for alkyl Al compounds; [ACGIH] Not TIH in land-based spills, but TiH substance released when spilled in water; [ERG 2016]
NFPA
burn readily
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: