Trifluorochloroethylene
Agent Name
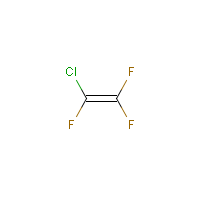
Trifluorochloroethylene
CAS Number
79-38-9
Formula
C2-Cl-F3
Major Category
Toxic Gases & Vapors
Synonyms
1,1,2-Trifluoro-2-chloroethylene; 1-Chloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethylene; 2-Chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethylene; CFE; CTFE; Chlorotrifluoroethylene; Chlortrifluoraethylen [German]; Daiflon; Ethene, chlorotrifluoro-; Ethylene, chlorotrifluoro-; Ethylene, trifluorochloro-; Fluoroplast 3; Genetron 1113; Monochlorotrifluoroethylene; Trifluorchlorethylen [Czech]; Trifluoromonochloroethylene; Trifluorovinyl chloride; Trithene; UN1082; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Other Toxic Gases & Vapors
Description
Colorless gas with a faint, ethereal odor; [Hawley] Shipped as a clear, colorless liquid; [CHEMINFO MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used to make chlorotrifluoroethylene resins (Kel-F, Halar); Used in the synthesis of lubricants, plastics, elastomers, and other chemical products; [HSDB]
Comments
Can cause frostbite; Inhalation can result in dizziness and nausea at lower concentrations and cardiac sensitization and CNS depression at higher concentrations; Liver and kidney injury may occur; Vapor can displace oxygen in a confined space and act as a simple asphyxiant; Decomposition products at temperatures >250 degrees C include hydrogen fluoride and phosgene; [CHEMINFO MSDS] Trifluorochloroethylene, stabilized (UN1082) has warning of explosive polymerization; [ERG 2016]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TIH
Yes
Vapor Pressure
4590 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 1,000 ppm/4H
Explosive Polymerization
Yes
Explanatory Notes
Boiling Point = -18 deg F; [CAMEO]
NFPA
burn readily
ERPG-1
20 ppm
ERPG-2
100 ppm
ERPG-3
300 ppm
WEEL
5 ppm
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Other Poison
Simple Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: