Phenylhydrazine hydrochloride
Agent Name
Phenylhydrazine hydrochloride
CAS Number
59-88-1
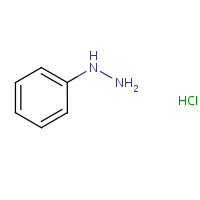
Formula
C6-H8-N2.Cl-H
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
Hydrazine, phenyl-, hydrochloride; Phenylhydrazin hydrochlorid [German]; Phenylhydrazine monohydrochloride; Phenylhydrazine-HCl; Phenylhydrazinium chloride; Hydrazine, phenyl-, monohydrochloride; [ChemIDplus] UN2572
Category
Hydrazines
Description
White to tan solid with a mild aromatic odor; [CAMEO] White powder; [Alfa Aesar MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Used to make dyes, antipyrine, and nitron (explosives stabilizer); as a reagent for sugars, aldehydes, and ketones; and as a therapeutic hemolytic; [Merck Index]
Comments
Causes cyanosis, corrosion, and weight loss in dermal lethal-dose studies of rabbits; Causes methemoglobinemia, respiratory stimulation, and normocytic anemia in intraperitoneal lethal-dose studies of rats; [RTECS] Overexposure may cause skin sensitization, hemolytic anemia, dyspnea, cyanosis, jaundice, kidney injury, vascular thrombosis, and occupational cancer; [Merck Index] An irritant and chronic poison; Ingestion may cause jaundice, anorexia, nausea, vascular thrombosis, anemia, and liver injury; [CHRIS] A skin and strong eye irritant; May cause skin sensitization; Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption; Risk of irreversible adverse health effects; Suspected to cause genetic defects and cancer; [Alfa Aesar MSDS] See "Phenylhydrazine."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Explanatory Notes
The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Phenylhydrazine."
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: