Phosphoenolpyruvate
Agent Name
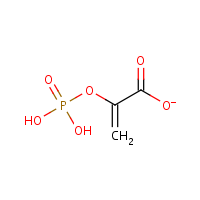
Phosphoenolpyruvate
CAS Number
73-89-2
Formula
C3-H4-O6-P
Major Category
Biological Agents
Synonyms
2-(Phosphonooxy)acrylate; 2-Propenoic acid, 2-(phosphonooxy)-, ion(1-); [ChemIDplus]
Category
Other Biomolecules
Sources/Uses
"Phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP), or phosphoenolpyruvate as the anion, is an important chemical compound in biochemistry. It has the highest-energy phosphate bond found (-61.9 kJ/mol) in living organisms, and is involved in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In plants, it is also involved in the biosynthesis of various aromatic compounds, and in carbon fixation; in bacteria, it is also used as the source of energy for the phosphotransferase system." [Wikipedia]
Biomedical References
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Other Information
No other related information on this agent was found.