Nitrogen mustard (HN-1)
Agent Name
Nitrogen mustard (HN-1)
Alternative Name
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ethylamine
CAS Number
538-07-8
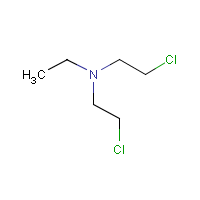
Formula
C6-H13-Cl2-N
Major Category
Toxic Gases & Vapors
Synonyms
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ethylamine; 2-Chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethylethanamine; 2,2'-Dichlorotriethylamine; Ethylbis(2-chloroethyl)amine; Ethyl-S; [ATSDR-MMG]
Category
Chemical Weapons
Description
Colorless to pale yellow, oily liquid with a faint fishy or musty odor; [ATSDR-MMG]
Sources/Uses
"Nitrogen mustards were first developed in the late 1920s and early 1930s. HN-1 was originally designed to remove warts but was later identified as a potential chemical warfare agent; None of the nitrogen mustards have been used on the battlefield, and none are included in U.S. stockpiles." [ATSDR MMG]
Comments
"Nitrogen mustards are vesicants causing skin, eye, and respiratory tract injury. Although these agents cause cellular changes within several minutes of contact, the onset of pain and other clinical effects is delayed for hours. Nitrogen mustards are alkylating agents that may cause bone marrow suppression and neurologic toxicity. . . . Nitrogen mustards may decrease fertility." [ATSDR MMG] Causes lachrymation; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TIH
Yes
Vapor Pressure
0.25 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
LCt50 = 1,500 mg-min/m³; [ATSDR-MMG] VP from ChemIDplus;
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Aplastic anemia
Lachrymator
Yes
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Probable (2a)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: