Methyl mercaptan
Agent Name
Methyl mercaptan
Alternative Name
Methanethiol
CAS Number
74-93-1
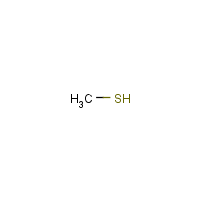
Formula
C-H4-S
Major Category
Toxic Gases & Vapors
Synonyms
Mercaptomethane; Methyl sulfhydrate; Methanethiol; Thiomethanol; Thiomethyl alcohol; [ChemID] UN1064
Category
Other Toxic Gases & Vapors
Description
Colorless gas with a disagreeable odor like garlic or rotten cabbage; Note: A liquid below 43 degrees F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as an odorant for some gases which are hazardous and odorless; used in the production of pesticides, jet fuel, plastics, and other organic chemicals; methyl mercaptan is a byproduct of the Kraft or sulfate process in paper and pulp production; [ACGIH] Produced from decaying organic matter and by pulp mills and oil refineries; [CAMEO]
Comments
A pulmonary irritant that can cause pulmonary edema after inhalation of high concentrations; Liver injury has been documented after occupational exposure. In high concentrations methyl mercaptan can cause coma and death, acting as a chemical asphyxiant similar to hydrogen sulfide. [ACGIH] Methemoglobinemia has been reported after occupational exposure. [HSDB] Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TIH
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.5 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
Ceiling(OSHA) = 10 ppm
MAK
0.5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
150 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: Students accidentally exposed to about 4 ppm for several hours experienced headaches and nausea [Clayton and Clayton 1981]. Some investigators have reported that the toxicity of methyl mercaptan is similar to hydrogen sulfide while others report the toxicity to be somewhat less than hydrogen sulfide [DeRekowski 1893; Frankel 1921].
Odor Threshold Low
2E-07 ppm
Odor Threshold High
0.04 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 675 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.00054 ppm); Flash point = -18 deg C;
Half Life
No reports found; [TDR, p. 893]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
burn readily
ERPG-1
0.002 ppm
ERPG-2
30 ppm
ERPG-3
100 ppm
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Other Poison
Chemical Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: