1-Decanesulfonic acid, sodium salt
Agent Name
1-Decanesulfonic acid, sodium salt
CAS Number
13419-61-9
Formula
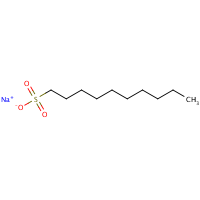
C10-H22-O3-S.Na
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
Sodium decane-1-sulphonate; [ChemIDplus] Sodium decane-1-sulfonate; [SIDS Dossier]
Category
Sulfonates, Alkane and Alkene
Description
93% by weight: Colorless or yellowish solid; [SIDS Dossier] White hygroscopic crystals; [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS]
Sources/Uses
Alkane sulfonates: Used in liquid detergents, concentrated shampoos, textile and leather auxiliaries (mercerising), metal cleaning preparations, steam jets, and pickling bathes; [SIDS Dossier]
Comments
Other common forms are 30-32% solutions and 60-62% pastes; Highly concentrated formulations are severely irritating or corrosive to skin; Concentrations greater than 10% cause permanent eye injury; [SIDS Dossier] No information available for this specific compound; Evaluated in the group of alkyl sulfates, alkane sulfonates, and alpha-olefin sulfonates (anionic surfactants); Acute LD50 values likely between 1,000 and 2,000 mg/kg for oral administration and greater than 500 mg/kg for dermal, based on studies using related compounds; Effects observed in oral lethal-dose studies of mice include non-specific clinical signs (lethargy, decreased motor activity and respiratory rate, and diarrhea), gastrointestinal tract irritation, and anemia of inner organs; Clinical effects observed in dermal lethal-dose studies of rabbits include severe skin irritation, tremor, clonic-tonic convulsions, and respiratory failure; Members of the group exhibited corrosive effects to rabbit skin and severe eye irritation with permanent corneal effects; Not expected to be a skin sensitizer; The liver was the target organ of toxicity in repeated dose oral studies, with effects including increased relative weight, hepatocyte hypertrophy, and elevated liver enzymes; Not likely to be mutagenic, carcinogenic, or a reproductive or developmental (in the absence of maternal toxicity) toxicant; [OECD SIDS] A skin and strong eye irritant; [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS]
Biomedical References
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: