n-Butylamine
Agent Name
n-Butylamine
CAS Number
109-73-9
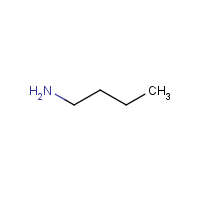
Formula
C4-H11-N
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1-Amino-butaan [Dutch]; 1-Aminobutan [German]; 1-Aminobutane; 1-Butanamine; Butylamine; Mono-n-butylamine; Monobutilamina [Romanian]; Monobutylamine; Norvalamine; n-Butilamina [Italian]; n-Butylamin [German]; n-Butylamine; [ChemIDplus] UN1125
Category
Amines, Aliphatic
Description
Colorless liquid with a fishy ammonia-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, drugs, rubber additives, emulsifiers, tanning agents, and insecticides; also used as a vulcanizing accelerator for rubber and as a curing agent for polymers; [NIOSH Guidelines for Chemical Hazards]
Comments
Liquid will burn skin; [CHRIS] Highly corrosive to skin; [Quick CPC] n-Butylamine can cause severe skin and eye burns as well as respiratory tract irritation and, potentially, pulmonary edema. [ACGIH] A corrosive substance that can cause pulmonary edema; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
Ceiling (ACGIH)
5 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
Ceiling(OSHA) = 5 ppm
MAK
2 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
300 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other animal data: Rats have survived a 4hour exposure to 2,000 ppm [Cheever et al. 1982]. It has been stated that butylamine is more than twice as toxic as ethylamine by the respiratory route [ACGIH 1991].
Vapor Pressure
92.9 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.08 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 4,000 ppm/4H
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.080 ppm); Odordetectable at 0.12 ppm; strong at 3-10 ppm. [ACGIH] Flash point = 10 deg F; VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
NFPA
may ignite at ambient temp
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: