p-Phenylenediamine
Agent Name
p-Phenylenediamine
CAS Number
106-50-3
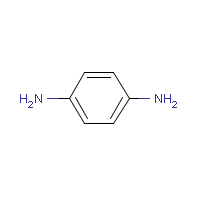
Formula
C6-H8-N2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1,4-Diaminobenzene; 1,4-Phenylenediamine; 4-Aminoaniline; 6PPD; AI3-00710; BASF ursol D; Benzofur D; C.I. 76060; C.I. Developer 13; C.I. Oxidation Base 10; CI 76060; CI Developer 13; CI Oxidation Base 10; Developer 13; Developer PF; Durafur Black R; FUR Brown 41866; Fenylenodwuamina [Polish]; Fouramine D; Fourrine 1; Fourrine D; Fur Black 41866; Fur Black 41867; Fur Yellow; Furro D; Futramine D; Nako H; Orsin; Oxidation Base 10; PARA; Paraphenylen-diamine; Paraphenylenediamine; Pelagol D; Pelagol DR; Pelagol Grey D; Peltol D; Phenylenediamine; Renal PF; Rodol D; Santoflex IC; Santoflex LC; Tertral D; USAF EK-394; Ursol D; Vulkanox 4020; Zoba Black D; p-Aminoaniline; p-Benzenediamine; p-Diaminobenzene; p-Fenylendiamin [Czech]; p-Phenyldiamine; p-Phenylenediamine; UN1673; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Amines, Aromatic
Description
White to slightly red, crystalline solid; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used to dye hair and fur; also used to develop photographs and to synthesize other organic compounds; [ACGIH] Occupational asthma reported in fur dyers; [Malo] Allergic contact dermatitis in hairdressers, mechanics, printers, and textile workers; [Marks] Used to dye leather; [PMID 21938525]
Comments
An important dye used for permanent hair coloring, the dye itself (but not the dyed hair) can cause allergic contact dermatitis. [Marks, p. 111] Immunologic contact urticaria documented; [Kanerva, p. 219] In animal experiments, intraperitoneal injections induce methemoglobinemia, and chronic feeding causes fatty degeneration of the liver. Liver injury after occupational exposure has been reported. [ACGIH] Potential adverse effects include asthma, allergic contact dermatitis, methemoglobinemia, and kidney injury; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
0.1 mg/m3
MAK
0.1 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
IDLH (NIOSH)
25 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for revised IDLH: No inhalation toxicity data are available on which to base an IDLH for pphenylene diamine. Therefore, based on health considerations and acute oral toxicity data in animals [Burnett et al. 1977; Hanzlik 1923; Lloyd et al. 1977], a value of about 50 mg/m3 would have been appropriate. However, the revised IDLH for pphenylene diamine is 25 mg/m3 based on the concentration recommended originally in the Standards Completion Program for deciding when the "most protective" respirators should be used. Because sensitized workers may be affected by concentrations far below occupational exposure limits, exacerbation of asthma cannot be used to set an IDLH.
Vapor Pressure
0.005 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 920 mg/m3/4H
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 311 deg F; VP less than 1 mm Hg at 21 deg C (technical product); [HSDB]
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Asthma
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: