DDT
Agent Name
DDT
Alternative Name
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
CAS Number
50-29-3
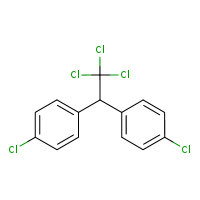
Formula
C14-H9-Cl5
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; 1,1'-(2,2,2-Trichloroethylidene)bis(4-chlorobenzene); 1,1,1-Trichloor-2,2-bis(4-chloor fenyl)-ethaan [Dutch]; 1,1,1-Trichlor-2,2-bis(4-chlor-phenyl)-aethan [German]; 1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-bis(4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl)ethane; 1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane; 1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane; 1,1,1-Trichloro-2,2-di(4-chlorophenyl)-ethane; 1,1,1-Tricloro-2,2-bis(4-cloro-fenil)-etano [Italian]; 1,1,1-Tricloro-2,2-bis(4-cloro-fenyl)-etano [Italian]; 1,1-Bis-(p-chlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trichloroethane; 2,2-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-1,1,1-trichloroethane; 4,4'-DDT; 4,4'-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; Aavero-extra; Agritan; Anofex; Arkotine; Azotox M 33; Benzochloryl; Bosan Supra; Bovidermol; Chlofenotan; Chlorophenothan; Chlorophenothane; Chlorophenothanum; Chlorophenothanum technicum; Chlorophenotoxum; Chlorphenothan; Chlorphenotoxum; Citox; Clofenotane; Clofenotane technique; Clofenotano [INN-Spanish]; Clofenotanum [INN-Latin]; D.D.T. technique; DDT 50 WP; Deoval; Detox; Detox (pesticide); Detoxan; Dibovin; Dicophane; Didigam; Didimac; Dodat; Dykol; Estonate; Ethane, 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-; Ethane, 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)-; Genitox; Gesafid; Gesarol; Guesarol; Gyron; Hildit; Ivoran; Ixodex; Klorfenoton [Swedish Pharmacopoeia]; Kopsol; Mutoxan; Neocid; Neocid (VAN); Neocidol; Neocidol (solid); OMS 0016 [French]; OMS 16; PEB1; Parachlorocidum; Pentachlorin; Pentech; Penticidum; Rukseam; Santobane; Tafidex; Trichlorobis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane; Zerdane; alpha,alpha-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-beta,beta,beta-trichloroethane; p'-Zeidane [France]; p,p'-DDT; p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Organochlorine Pesticides
Description
Colorless crystals or off-white powder with a slight, aromatic odor. [pesticide]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Formerly used as an insecticide and pesticide; [HSDB]
Comments
Still used in some parts of the world, DDT persists in the environment and in animal tissues. It has been especially harmful to predator species of birds. High-dose animal studies show that organochlorine insecticides are toxic to the liver. [LaDou, p. 553] Allergic contact dermatitis reported in farmworkers; [Kanerva, p. 1777] "Despite the billions of pounds of DDT that have been manufactured and used, hepatic injury acquired as the result of occupational or environmental exposure to it remains to be reported." [Zimmerman, p. 413]
Restricted
All agricultural uses cancelled in 1972 by EPA; [Sullivan, p. 660]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
Bioaccumulates
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
1 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
1 mg/m3
MAK
1 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
IDLH (NIOSH)
500 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: Exposure of volunteers to 423 mg/m3 for periods of 1 hour/day for 6 days has been reported to only cause eye irritation [Neal et al. 1994]. It has been reported that 500 mg/kg is the lethal oral dose [Windholz 1983]. [Note: An oral dose of 500 mg/kg is equivalent to a 70kg worker being exposed to about 23,000 mg/m3 for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
1.6E-07 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
VP from HSDB;
Half Life
1-2 years to eliminate absorbed dose; [TDR, p. 440]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Probable (2a)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Other Poison
Organochlorine
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: