1,2,3,7,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Agent Name
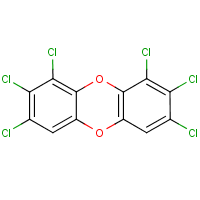
1,2,3,7,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
CAS Number
19408-74-3
Formula
C12-H2-Cl6-O2
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
1,2,3,7,8,9-Hexachlorodibenzo(b,e)(1,4)dioxin; D 70; Dibenzo-p-dioxin, 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachloro-; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Halogenated Polyaromatics
Description
Light pink solid; [CAMEO] Orange powder; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Found in emissions from waste incineration, PCB’s, automobiles (using leaded gas), and improper waste disposal of some chlorinated compounds; Not commercially produced; [HSDB] Hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins (HCDD): Found as impurities in polychlorinated phenols and chlorophenol derivative herbicides (i.e. 2,4-D); [NTP]
Comments
Can cause chloracne and liver injury; [CAMEO] Polychlorodibenzodioxins have caused chloracne in humans; Oral LD50 (rat) = 1.8 (male) and 0.8 (female) mg/kg bw (31% 1,2,3,6,7,8- and 67% 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins); [HSDB] No evidence of carcinogenicity in mice with dermal application, but carcinogenic effects, including hepatocellular carcinomas, observed in gavage study with rats and mice (mixture of 1,2,3,6,7,8- and 1,2,3,7,8,9-hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxins); [NTP] IARC classification is for polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins other than 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD);
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
4.88E-11 mm Hg
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Chloracne
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: