Ethanolamine
Agent Name
Ethanolamine
Alternative Name
2-Aminoethanol
CAS Number
141-43-5
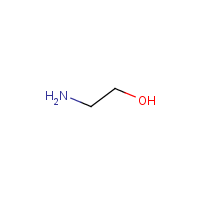
Formula
C2-H7-N-O
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1-Amino-2-hydroxyethane; 2-Amino-1-ethanol; 2-Aminoaethanol [German]; 2-Aminoetanolo [Italian]; 2-Aminoethanol; 2-Hydroxyethanamine; 2-Hydroxyethylamine; Aethanolamin [German]; Aminoethanol; Colamine; Etanolamina [Italian]; Ethanol, 2-amino-; Ethanolamine; Ethylolamine; Glycinol; Glycinol (monoethanolamine); Kolamin [Czech]; MEA (alcohol); Monoaethanolamin [German]; Monoethanolamine; Olamine; Thiofaco M-50; beta-Aminoethyl alcohol; beta-Hydroxyethylamine; [ChemIDplus] UN2491
Category
Ethanolamines
Description
Colorless, viscous liquid or solid (below 51 degrees F) with an unpleasant, ammonia-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a scavenger for CO2 and H2S in natural gas; used in the synthesis of surface active agents, hair waving agents, hide softeners, agricultural chemicals, and antibiotics; [Merck Index, # 3727] Used in soaps, cosmetics, polishes, paints, cutting oils, and textile processing; [HSDB] Used in photography (color developing bath); [www.ci.tucson.az.us/arthazards/medium.html]
Comments
Liquid causes first degree burns on short exposure; [CHRIS] Ethanolamine is a skin irritant. [Quick CPC] Occupational asthma reported in hairdressers; [Malo] Toxic to the liver in subchronic inhalation studies of animals; [ACGIH] It is an irritant, but allergic contact dermatitis has been reported. [Kanerva, p. 1817] A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; Inhalation of high concentrations can cause CNS depression; Can cause skin sensitization; [ICSC] Danger of skin sensitization; [MAK]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
3 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
6 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
3 ppm
MAK
0.2 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
30 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other animal data: Cats exposed for 2 hours to vapors of ethanolamine at concentrations reaching 970 ppm displayed vomiting tendencies; mice had no adverse effects from the same exposures [Sidorov et al. 1968]. A single 8hour exposure to "concentrated vapors" did not kill any of six rats [UCC 1970]. Guinea pigs survived a 15minute exposure to ethanolamine at 193 ppm [Treon et al. 1957].
Vapor Pressure
0.4 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
2.6 ppm
Odor Threshold High
5 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (mice) > 2,420mg/m3/2H
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold (detect at 2.6 ppm and recognize at 5 ppm) from CHEMINFO; Flash point = 86 deg C; VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Asthma
Yes
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes