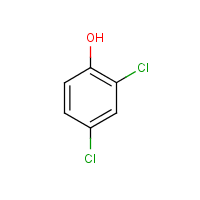
2,4-Dichlorophenol
Agent Name
2,4-Dichlorophenol
CAS Number
120-83-2
Formula
C6-H4-Cl2-O
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
1-Hydroxy-2,4-dichlorobenzene; 2,4-DCP; 2,4-Dichlorohydroxybenzene; 4,6-Dichlorophenol; Phenol, 2,4-dichloro-; [ChemIDplus] UN2020
Category
Chlorophenols
Description
Colorless to pale yellow solid with a strong medicinal odor; Melts at 45 deg C; [HSDB] Crystalline solid; mp = 65-68 deg C; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used to make herbicides, dyestuffs, mothproofing agents, antiseptics, seed disinfectants, miticides, wood preservatives, and the antihelminthic bithionol sulfoxide; According to a 1982 report, it was being used in the following industries: wood treatment, tanneries, textile plants, pulp and paper mills, and pesticide services; [HSDB]
Comments
A corrosive substance that can cause injury to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; "Exposure to small amounts of the molten or liquid form of the substance may result in extensive skin absorption and rapid death." [ICSC] A corrosive substance that can cause injury to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; Inhalation may cause chemical pneumonitis; May be absorbed through skin; Effects in high-dose animal studies include acute tubular necrosis and convulsions; [MSDSonline] The mechanism of toxicity is uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation; Lethal dose is approximately 21 grams or a skin splash of 15 ml of molten 2,4-DCP; [AIHA] See "CHLOROPHENOLS."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
0.116 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 113 deg C; [Hawley] The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Chlorophenols, solid." VP from ChemIDplus;
NFPA
must be preheated
ERPG-1
0.2 ppm
ERPG-2
2 ppm
ERPG-3
20 ppm
WEEL
1 ppm
Adverse Effects
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
Other Poison
Uncoupler
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: