Dicloran
Agent Name
Dicloran
Alternative Name
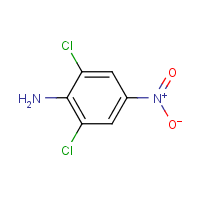
2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline
CAS Number
99-30-9
Formula
C6-H4-Cl2-N2-O2
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
2,6-Dichloro-4-nitroaniline; 2,6-Dichlor-4-nitroanilin [Czech]; 2,6-Dichloro-4-nitrobenzenamine; 4-Nitro-2,6-dichloroaniline; 4-Nitroaniline, 2,6-dichloro-; AL-50; Allisan; Batran; Bortran; Botran; Botran 45W; CAN; DCNA; DCNA (fungicide); Dichloran; Dichloran (amine fungicide); Dicloran [BSI]; Ditranil; RD-6584; Resisan; U-2069; [ChemIDplus] UN2237
Category
Fungicides
Description
Yellow, odorless solid; [ICSC] Technical grade (>90% purity) is brownish yellow; [CHEMINFO]
Sources/Uses
Used as a selective agricultural fungicide by soil treatment, foliage spray, or dust for vegetables and fruits; Also used to make yellow-brown disperse dyes; [HSDB] Used as an indicator; [CHEMINFO]
Comments
A skin, eye, and respiratory tract irritant; [ICSC] Effects in high-dose animal studies include convulsions, methemoglobinemia, and liver injury; [RTECS] "No indication that administration of dicloran at 10 mg/day to men for 90 days had any adverse effect. Extensive examinations were made on one industrial worker occupationally exposed to dicloran over three years, with considerable inhalation and dermal exposure for about 60 days/year. No adverse effects were observed." [Reference #1]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
1.2E-06 mm Hg
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) > 5,400 mg/m3/4h
Explanatory Notes
The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Chloronitroanilines."
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: