Chlorobromomethane
Agent Name
Chlorobromomethane
Alternative Name
Bromochloromethane
CAS Number
74-97-5
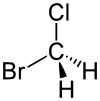
Formula
C-H2-Br-Cl
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Bromochloromethane; Chloromethyl bromide; Fluorocarbon 1011; Halon 1011; Methane, bromochloro-; Methylene chlorobromide; Mil-B-4394-B; Mono-chloro-mono-bromo-methane; [ChemIDplus] UN1887
Category
Chlorofluorocarbons
Description
Colorless to pale-yellow liquid with a chloroform-like odor; Note: May be used as a fire extinguishing agent; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used in fire extinguishers; [ACGIH]
Comments
In animal studies, causes reversible liver injury, narcosis, and anesthesia; Fire fighters exposed to high concentrations lost consciousness. [ACGIH]
Restricted
See CHLOROFLUOROCARBONS
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
200 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
200 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
2000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: Patty [1963] reported that light narcosis could be produced in animals at 3,000 ppm, and pulmonary edema and deaths during exposure at 27,000 ppm; delayed deaths occurred after exposure to 20,000 ppm [Comstock et al. 1953]. Patty [1963] also reported that guinea pigs survived 1hour exposures but 1 of 3 guinea pigs died after 2hour exposures to 8,000 to 10,000 ppm [Matson and Dufour 1948]. . . . Basis for revised IDLH: The revised IDLH for chlorobromomethane is 2,000 ppm based on acute inhalation toxicity data in animals [Comstock et al. 1952; Comstock and Oberst 1953; Matson and Dufour 1948]. This may be a conservative value due to the lack of relevant acute toxicity data for workers.
Vapor Pressure
142 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
397 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 28,800 ppm/15 min
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from ACGIH; VP from HSDB;
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: