Cyanogen
Agent Name
Cyanogen
CAS Number
460-19-5
Formula
C2-N2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
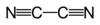
Synonyms
Dicyan; Dicyanogen; Ethanedinitrile; Oxalonitrile; [NIOSH] Oxalic acid dinitrile
Carbon nitride; Oxalyl cyanide; Prussite; Nitriloacetonitrile; [CHEMINFO] UN1026
Category
Nitriles
Description
Colorless gas with a pungent, almond-like odor. [Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas. Forms cyanide in the body.] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used in organic synthesis; Also used as a fuel (for cutting and welding heat-resistant metals), a rocket fuel, and a fumigant; Produced in internal combustion engines burning gasoline with nitrogen additives and in blast furnaces; [ACGIH]
Comments
Hydrolysis of cyanogen yields hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and cyanate. Toxic effects are due to HCN. TLV Basis: eye and upper respiratory tract irritation; "Subchronic inhalation exposure of 15 monkeys and 90 rats, divided into 3 groups of 5 monkeys and 30 rats exposed 6 hours/day, 5 days/week for 6 months at 25 ppm of cyanogen was marginally toxic as evidenced from decreased body weight, which was not observed in the animals exposed to 11 ppm." [ACGIH] Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH] A lachrymator; [CHEMINFO] See "NITRILES."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TIH
Yes
Ceiling (ACGIH)
5 ppm
MAK
5 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 = 350 ppm/1h
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold is >250 ppm; Eye & nasal irritation @ 16 ppm; A 2-hr exposure @ 250 ppm killed all rats within 14 days. Rats exposed to 25 ppm for 6 months show significant weight loss. [CHEMINFO]
NFPA
burn readily
Adverse Effects
Lachrymator
Yes
Other Poison
Chemical Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: