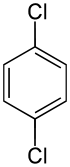
p-Dichlorobenzene
Agent Name
p-Dichlorobenzene
Alternative Name
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
CAS Number
106-46-7
Formula
C6-H4-Cl2
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
p-DCB; para-Dichlorobenzene; Dichlorocide; 1,4-Dichlorobenzene; [NIOSH]
Category
Fumigants
Description
Colorless or white crystalline solid with a mothball-like odor. [insecticide]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as an insecticide and fumigant; [ACGIH] Used as a deodorizer for toilets and garbage cans; Also used as a moth repellent and chemical intermediate; [CHEMINFO]
Comments
After daily doses of 500 mg/kg, rats develop focal hepatic necrosis. TLV Basis: eye irritation and kidney damage; Humans report eye irritation at 17 ppm and higher. Renal toxicity is observed in animal experiments at 25 ppm and higher. Hemolytic anemia, methemoglobinuria, and jaundice have been reported after ingestion. [ACGIH] Experimental animals suffer CNS depression and liver and kidney damage after high-dose inhalation studies. [CHEMINFO] Suspected germ cell mutagen (3B); [MAK]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
75 ppm
MAK
2 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
150 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
No adverse effects were noted in a workplace averaging 105 ppm (range 50 to 170 ppm), but painful irritation of the eyes and nose was found at 80 to 160 ppm, and breathing was difficult at concentrations greater than 160 ppm [Hollingsworth et al. 1956].
Vapor Pressure
1.74 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.12 ppm
Odor Threshold High
15 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 0.12 ppm); Melting point = 53 deg C; [CHEMINFO] VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: