Dichloroethyl ether
Agent Name
Dichloroethyl ether
Alternative Name
2,2'-Dichlorodiethyl ether
CAS Number
111-44-4
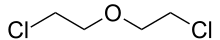
Formula
C4-H8-Cl2-O
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
2,2'-Dichlorodiethyl ether; Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether; 2,2`-Dichloroethyl ether; 2,2'-Dichlorodiethyl ether; [NIOSH] UN1916
Category
Halogenated Ethers
Description
Colorless liquid with a chlorinated solvent-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent, dewaxing agent, wetting agent, soil fumigant, and chemical intermediate; [ACGIH] Used to control earworms on corn silks; No longer used as a soil fumigant; [HSDB]
Comments
Damage to the lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain occur in studies of guinea pigs and rats at 500 ppm for 5 to 8 hours. Volunteers found exposures above 550 ppm intolerable because of nauseating odor and irritation of the eyes, nose, and respiratory tract. [ACGIH] The vapor can cause lacrimation.[HSDB] A severe eye irritant; [CHEMINFO] "Some animal studies indicate that bis(2-chloroethyl) ether can affect the nervous system resulting in sluggish and slow movement, staggering, unconsciousness, and death." [ATSDR - ToxFAQs]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
5 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
Ceiling(OSHA) = 15 ppm
MAK
0.5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
100 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Basis for original (SCP) IDLH: The chosen IDLH is based on the statements by Patty [1963] that 250 ppm caused death in rats from a 4hour exposure [Carpenter et al. 1949] and that 500 to 1000 ppm might cause death in guinea pigs from an exposure of only 30 to 60 minutes duration [Schrenk et al. 1933]. . . . Human data: Volunteers found brief (undefined) exposures to 100 to 260 ppm to be tolerable, although irritating [Schrenk et al. 1933].
Vapor Pressure
1.55 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.049 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 330 mg/m3/4H
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from CHEMINFO; VP from HSDB;
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Lachrymator
Yes
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Not classifiable
ACGIH Carcinogen
Not Classifiable
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: