2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Agent Name
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
Alternative Name
TCDD
CAS Number
1746-01-6
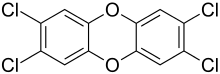
Formula
C12-H4-Cl4-O2
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
2,3,7,8-Czterochlorodwubenzo-p-dwuoksyny [Polish]; 2,3,7,8-TCDD; 2,3,7,8-Tetra polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin; 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo(b,e)(1,4)dioxin; 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-1,4-dioxin; 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin [Dioxin and dioxin-like; compounds]; 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin; Dibenzo(b,e)(1,4)dioxin, 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro-; Dibenzo-p-dioxin, 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro-; Dioksyny [Polish]; Dioxin; Dioxin (herbicide contaminant); Dioxine; TCDBD; TCDD; Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; Tetrachlorodibenzodioxin; Tetradioxin; [ChemIDplus] UN2811
Category
Halogenated Polyaromatics
Description
Colorless to white, crystalline solid; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
No commercial uses; By-product of waste incineration, pulp and paper mill bleaching, and chemical production of 2,4,5-T, hexachlorophene, vinyl chloride, trichlorophenol, and pentachlorophenol; [Reference #2, p. 377] Levels in 2,4,5-T manufactured in the 1960s was as high as 100 mg/kg; High-exposure populations in the past included workers producing the herbicide 2,4,5-T and residents in Seveso, Italy contaminated by a factory explosion in 1976; [Reference #1]
Comments
Dioxins accumulate in adipose tissue; they are animal carcinogens. Chloracne is the only overt clinical sign of dioxin exposure in humans. Of the 22 isomers of tetra-chlorinated dioxin, 2,3,7,8-TCDD is the one that contaminated the production of 2,4,5-trichlorophenol, Silvex, and 2,4,5-T. In acute animal studies, TCDD is toxic to the liver. Recent studies failed to find an association between TCDD and porphyrin levels; [LaDou, p. 517-20] Causes adverse reproductive effects in animals; No documented evidence of congenital abnormalities in humans; [REPROTOX] "There are no firmly established relationships between concentrations (mainly considering TCDD) and health effects in people. Observations following industrial and accidental exposures have suggested that acute exposures resulting in serum concentrations of about 800 pg/g of lipid might be necessary to induce clinical effects such as chloracne, although levels in the thousands of pg/g of lipid do not always produce this effect." [Reference #2, p. 384] IARC classification for 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin is "known" and for other isomers is " not classifiable"; An increased risk for all cancers combined was found in the high-exposure populations studied; [Reference #1] The German MAK Commission classifies TCDD as class 4, defined as: "Substances with carcinogenic potential for which genotoxicity plays no or at most a minor role. No significant contribution to human cancer risk is expected, provided the MAK value is observed. " [Guide to Occupational Exposure Values, p. xi] Mean levels in exposed workers were 2000 ppt in the US cohort, 1434 ppt in accident workers in the Dutch cohort, and 1008 ppt in the BASF workers (Germany) with chloracne. Levels were up to 2252 ppt in the Boehringer cohort (Germany). These levels are comparable to levels in rats that developed hepatocellular nodules when fed 10 ng/kg bw daily (1500-2000 ppt) and that developed hepatocellular carcinoma when fed 100 ng/kg/bw daily (5,000-10,000 ppt). [Reference #1] Among 773 pentachlorophenol workers exposed to chlorinated dioxins from 1937 to 1980 with up to 64 years of follow-up, no increased mortality was found except for possibly an increased risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma based on 4 deaths. [PMID 19786897]
Restricted
NIOSH recommends lowest feasible level of exposure. TCDD product contamination is limited to 0.01 to 0.05 ppm. For drinking water, MCL is 0.05 ppt. FDA limit for dioxins in fish is 25 ppt. [ATSDR Case Studies]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Bioaccumulates
Yes
MAK
1E-08 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
Vapor Pressure
1.5E-09 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Whole body: 7.1 years (2.9 to 26.9 years); [TDR, p. 1111] Estimated at around 7 years; [Reference #2, p. 379]
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Chloracne
IARC Carcinogen
Established
NTP Carcinogen
Human carcinogen
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: