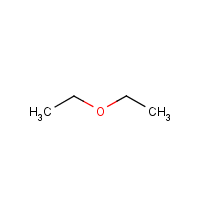
Ethyl ether
Agent Name
Ethyl ether
Alternative Name
Diethyl ether
CAS Number
60-29-7
Formula
C4-H10-O
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Diethyl ether; 1,1'-Oxybisethane; 3-Oxapentane; Aether; Anaesthetic ether; Anesthesia ether; Anesthetic ether; Diaethylaether [German]; Diethyl oxide; Dwuetylowy eter [Polish]; Etere etilico [Italian]; Ethane, 1,1'-oxybis-; Ether; Ether ethylique [French]; Ether, ethyl; Ethoxyethane; Ethyl ether; Ethyl ether, tech.; Ethyl oxide; Oxyde d'ethyle [French]; Pronarcol; Solvent ether; [ChemIDplus] UN1155
Category
Ethers (<C12)
Description
Colorless liquid with a pungent, sweetish odor; Note: A gas above 94 degrees F; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent and a reagent in organic syntheses; [ACGIH] Used as a solvent (waxes, fats, oils, perfumes, gums, nitrocellulose, alkaloids); Also used to prime gasoline engines; [Merck Index]
Comments
Abnormal liver function tests has been reported in patients anesthetized with ethyl ether. Abuse of ether by workers, "ether jags," has been reported. [ACGIH] Ethyl ether is in the list of "Some volatile substances which may be abused by inhalation" published on the web site of the U.N. International Drug Control Programme, indicating its potential to cause narcosis in workers. [Reference #1] An eye and respiratory tract irritant; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
400 ppm
STEL (ACGIH)
500 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
400 ppm
MAK
400 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
1900 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: The lowest anesthetic limit is 19,000 ppm [Clayton and Clayton 1981]. It has been stated that the inhalation of 2,000 ppm if continued to equilibrium in the blood would cause dizziness in some persons [Henderson and Haggard 1943]. Concentrations in the workplace of 500 to 1,000 ppm or more have not resulted in demonstrable injury to health [Cook 1945]. It has been reported that the inhalation of 35,000 ppm causes loss of consciousness within 30 to 40 minutes, and concentrations above 75,000 ppm are dangerous to life [Pennsylvania 1973].
Vapor Pressure
538 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
0.3 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LCLo (rat) = 32,000 ppm/4h
Explanatory Notes
IDLH = 10% LEL; Odor threshold (100% recognition) from CHEMINFO; Flash point = -45 deg C; VP from HSDB;
NFPA
burn readily
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: