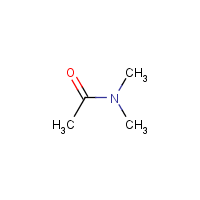
Dimethyl acetamide
Agent Name
Dimethyl acetamide
Alternative Name
N,N-Dimethylacetamide
CAS Number
127-19-5
Formula
C4-H9-N-O
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Acetamide, N,N-dimethyl-; Acetdimethylamide; Acetic acid, dimethylamide; Acetyldimethylamine; CBC 510337; DMA; DMAC; Dimethylacetamide; Dimethylacetone amide; Dimethylamid kyseliny octove [Czech]; Dimethylamide acetate; N,N-Dimethylacetamide; N,N-Dimethylethanamide; SK 7176; U-5954; [ChemIDplus] UN1993
Category
Amides (<C10)
Description
Colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent for "many organic reactions, resins, polymers, crystallization, and purification." [ACGIH] Used as a solvent in plastics, resins, and gums; Also used as a catalyst and paint remover; [Hawley] Used in synthetic fiber and resin industries; Used as a solvent in elastane fiber factories; [Reference #1]
Comments
Toxic hepatitis has been reported in workers after inhalation and dermal exposure. DMAC is fetotoxic and teratogenic when administered at high doses to rabbits and rats. NOAEL = 25 ppm for hepatic and renal toxicity in rats and mice. Humans exposed to high doses may experience mental confusion. [ACGIH] A skin and eye irritant; Inhalation of high concentrations may cause liver and CNS effects; [ICSC] In a study of 440 new elastone fiber workers, 28 cases with elevated liver enzymes were detected in a 31 month period from 2002 to 2004. Using the BEI of 30 mg/g creatinine as a cutoff, the incidence of hepatic injury was about 7 times greater in the high exposure group. [Reference #1]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
M-Methylacetamide in urine = 30 mg/g creatinine; end of shift at end of workweek;
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
10 ppm
MAK
5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
300 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
The chosen IDLH is based on the statement by Deichmann and Gerarde [1969] that acute inhalation at 406 and 575 ppm causes some deaths and degeneration of the liver in several species of laboratory animals. Although no time period is specified for that exposure, the chosen IDLH is probably reasonable, and perhaps even conservative, because Patty [1963] reported that liver injury was noted only in some rats and dogs exposed to repeated inhalation at 100 to 200 ppm [Horn].
Vapor Pressure
2 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
21 ppm
Odor Threshold High
47 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 2,475 ppm/1H
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from "Quick Guide: The Electronic NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards"; Flash point = 70 deg C; VP from HSDB;
NFPA
high ambient temp required
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Occupational hepatotoxin (principal effect)
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: