m-Dinitrobenzene
Agent Name
m-Dinitrobenzene
CAS Number
99-65-0
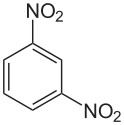
Formula
C6-H4-N2-O4
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1,3-Dinitrobenzene; 1,3-Dinitrobenzol; 2,4-Dinitrobenzene; Benzene, 1,3-dinitro-; Benzene, m-dinitro-; Dinitrobenzene; Dwunitrobenzen [Polish]; m-DNB; m-Dinitrobenzene; meta-Dinitrobenzene; [ChemIDplus] UN1597
Category
Nitros, Aromatic
Description
Pale-white or yellow, crystalline solid; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Usually manufactured as a mixture of 3 isomers, DNB is used to make dyes, explosives, celluloids, and organic chemicals; [ACGIH]
Comments
Methemoglobinemia, liver injury, and visual impairment (central scotomas) have been reported in exposed workers. Listed in table of "Industrial Chemicals for Which Methemoglobin Formation is the Principal Cause of Toxicity"; [ACGIH] m-Dinitrobenzene was eliminated from in vitro testing after little response was detected, even at high concentrations. [French CL et al. Potency ranking of methemoglobin-forming agents. J Appl Toxicol. 15(3):167-74 (1995).]; An eye and respiratory tract irritant; Can induce methemoglobinemia and have effects on the liver; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Methemoglobin in blood = 1.5% of hemoglobin during or at end of shift. [ACGIH]
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
1 mg/m3, inhalable fraction and vapor
PEL (OSHA)
1 mg/m3
IDLH (NIOSH)
50 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: The probable lethal oral dose has been reported to be 2 grams [Deichmann and Gerarde 1969]. [Note: An oral dose of 2 grams is equivalent to a worker being exposed to about 1,300 mg/m3 for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
0.0002 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 302 deg F; VP from HSDB;
Adverse Effects
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is primary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: