2,4-Diaminophenol dihydrochloride
Agent Name
2,4-Diaminophenol dihydrochloride
CAS Number
137-09-7
Formula
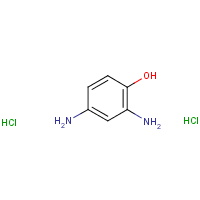
C6-H8-N2-O.2Cl-H
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
2,4-Diaminophenol HCl; 2,4-Diaminophenol hydrochloride; Acrol; Amidol; Diamidophenol hydrochloride; Dianol; Phenol, 2,4-diamino-, dihydrochloride; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Amino Phenols
Description
Grayish-white solid; [HSDB] Slightly gray crystalline solid; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used as photographic developer, analytical reagent, and in fur and hair dyeing; [HSDB]
Comments
Limited evidence of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity in male mice; No evidence of carcinogenicity in female mice or male and female rats; Emergency treatment: "Paraphenylenediamine"; In sensitized individuals, paraphenylenediamine may cause allergic contact dermatitis following application as a hair dye and asthma following inhalation; Following ingestion, can cause angioneurotic edema, methemoglobinemia, acute tubular necrosis, and hepatotoxicity; An adult died after ingestion of 3 grams of p-phenylenediamine; Another adult who ingested 1800 mg developed angioneurotic edema and acute renal failure; [HSDB] May cause irritation and allergic reactions; [CAMEO] Causes changes in liver and bladder weight, erythrocyte count, and levels of transaminases in high-dose feeding studies of mice; [RTECS] See "p-Phenylenediamine."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: