Echimidine
Agent Name
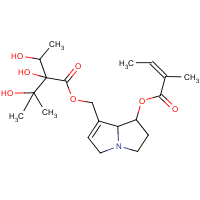
Echimidine
CAS Number
520-68-3
Formula
C20-H31-N-O7
Major Category
Biological Agents
Synonyms
2-Butenoic acid, 2-methyl-, 7-((2,3-dihydroxy-2-(1-hydroxyethyl)-3-methyl-1-oxobutoxy)methyl)-2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1H-pyrrolizin-1-yl ester; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Plant Toxins
Sources/Uses
A toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid found in plants; [INCHEM] More than 350 pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) in over 6000 plants have been identified. They are probably the most common cause of plant poisoning in the world and affect livestock, wildlife, and humans. They are found in the Boraginaceae, Compositae, and Leguminosae families and are commonly encountered in the following plants: fiddle neck, tarweed, rattle box, blue weed, giant hog weed, heliotrope, groundsels, Senecio, and comfrey. [Haddad, p. 494] Liver disease from "bush tea" derived from the Crotalaria plant is endemic in Jamaica. Cereal contaminated with PA seeds (Heliotropium and Crotalaria) have caused epidemics in Afghanistan and India. Herbal remedies that have caused liver disease include Senecio and comfrey. [Goldfrank, p. 647]
Comments
Emergency treatment: "Plants- pyrrolizidine alkaloids"; Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) cause veno-occlusive liver disease. Diagnosis is difficult because symptoms may be delayed for days or weeks. After drinking herbal tea or eating plants contaminated with seeds of PA plants, symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, and later cirrhosis and ascites. Jaundice may be present. Children may appear to have Reye's syndrome. [HSDB] The liver is the target organ. Plants containing significant amounts of pyrrolizidine alkaloids are found all over the world, comprising about 3% of all flowering plants. They have long been known to be toxic to livestock. Outbreaks of poisoning cases in humans after food contamination have been reported, and the problem is endemic in some central Asian republics. [Reference #1] Teas containing PAs include coltsfoot, comfrey, gordolobo, groundsel, mate, tansy ragwort, and T'u-san-chi. The teas may be prescribed as herbal remedies for anxiety or amenorrhea. The alkaloid is concentrated in the root of the plants. As little as 85 mg may be toxic. [Haddad, p. 1082]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Other Information
No other related information on this agent was found.