Hexachloronaphthalene
Agent Name
Hexachloronaphthalene
CAS Number
1335-87-1
Formula
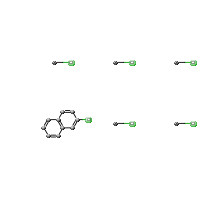
C10-H2-Cl6
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
Halowax 1014; [NIOSH]
Category
Halowaxes
Description
White to light-yellow solid with an aromatic odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as additives to lubricants and cable insulation (fire retardants); [ACGIH]
Comments
Chlorinated naphthalenes may be absorbed through the skin. They cause fatal liver injury in animals in subchronic inhalation studies. Penta- and hexachloronaphthalene may cause in exposed workers acne-like lesions that itch severely. Tri-, tetra-, and octachloronaphthalene are non-acnegenic under the conditions of industrial use. Nine occupational fatalities from chlorinated naphthalene poisoning have been reported. Most cases of intoxication among cable workers, assemblers, and laborers involve either penta- or hexachloronaphthalene. A nonfatal case of toxic hepatitis was reported in an 18 year old female who was soldering electrical condensers. [ACGIH] Acne-form dermatitis is listed as an adverse effect for all of the halowaxes except trichloronaphthalene in the NIOSH Pocket Guide.
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
Bioaccumulates
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.2 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
0.2 mg/m3
IDLH (NIOSH)
2 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Animal data: Repeated exposure of rats to 8.9 mg/m3 of a mixture of hexachloronaphthalene and pentachloronaphthalene for up to 4.5 months produced jaundice and was fatal; minor liver injury still occurred at 1.16 mg/m3 [Drinker et al. 1937]. Hexachloronaphthalene has been shown to be more toxic than pentachloronaphthalene in ingestion studies with calves [Bell 1958]. Total doses of hexachloronaphthalene ranging from 5 to 23 mg/kg were given orally in mineral oil over 10 days and lacrimation, salivation, nasal discharge, depression, and anorexia occurred by the 5th day [Bell 1958]. \
Human data: It has been reported that fatal cases of hepatic injury have occurred from chronic exposures in a plant where air concentrations of mixed pentachloronaphthalenes and hexachloronaphthalenes ranged from 1 to 2 mg/m3 [Elkins 1959].
Vapor Pressure
3.3E-06 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
VP from HSDB;
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Occupational hepatotoxin (principal effect)
Dermatotoxin
Chloracne
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: