Chloroform
Agent Name
Chloroform
Alternative Name
Trichloromethane
CAS Number
67-66-3
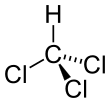
Formula
C-H-Cl3
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Methane trichloride; Trichloromethane; [NIOSH] Formyl trichloride; Methenyl trichloride; Methyl trichloride; Trichloroform; [CHEMINFO]
Category
Chlorinated Aliphatics
Description
Colorless liquid with a pleasant odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Has been used mainly for extraction and spot cleaning; [LaDou, p. 552] Used mainly in production of chlorodifluoromethane; [CHEMINFO] Uses have included dry cleaning agent and solvent for resins, plasticizers, rubber chemicals, and flavors; [HSDB]
Comments
Anesthesia is produced at concentrations of 10,000 ppm. Laboratory animals develop dose-dependent hepatic necrosis. Chloroform is embryotoxic in high-dose inhalation studies of pregnant rats. [ACGIH] Chloroform is in the list of "Some volatile substances which may be abused by inhalation" published on the web site of the U.N. International Drug Control Programme, indicating its potential to cause narcosis in workers. [Reference #1] Acute exposure to high concentrations of chloroform can cause liver and kidney injury, but much less than that caused by carbon tetrachloride. [Rosenstock, p. 575]
Restricted
No longer used as a fumigant in the U.S. [EPA Pesticides]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
10 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
Ceiling(OSHA) = 50 ppm
MAK
0.5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
500 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
It has been reported that inhalation of 10,000 ppm has produced clinical anesthesia [NIOSH 1974] and that exposure for 2 minutes to 1,107 ppm has caused dizziness and vertigo [Lehmann et al. 1936]. Workers exposed 4 hours/day to concentrations of 57 to 71 ppm complained of lassitude, loss of appetite, and nausea [Challen et al. 1958]. Exposures to 390 ppm were tolerated for 30 minutes without complaint, whereas 1,030 ppm resulted in dizziness, intracranial pressure, and nausea in 7 minutes, with headache for several hours [Lehmann and Flury 1943].
Vapor Pressure
197 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
133 ppm
Odor Threshold High
276 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 47,702 mg/m3/4H
Explanatory Notes
Detection odor threshold from AIHA (mean = 192 ppm); VP from HSDB;
Half Life
Whole body: 1.5 hours; [TDR, p. 318]
Reference Link #2
NFPA
will not burn
ERPG-1
Not appropriate
ERPG-2
50 ppm
ERPG-3
5,000 ppm
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
NTP Carcinogen
Anticipated human carcinogen
ACGIH Carcinogen
Confirmed Animal
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure:
Activities
Activities with risk of exposure: