Picric acid
Agent Name
Picric acid
Alternative Name
2,4,6-Trinitrophenol
CAS Number
88-89-1
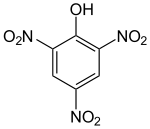
Formula
C6-H3-N3-O7
Major Category
Other Uses
Synonyms
1,3,5-Trinitrophenol; 2,4,6-Trinitrofenol [Dutch]; 2,4,6-Trinitrofenolo [Italian]; 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol; 2-Hydroxy-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene; Acide picrique [French]; Acido picrico [Italian]; Acidum picrinicum; C.I. 10305; CI 10305; Carbazotic acid; Kyselina pikrova [Czech]; Melinite; Nitroxanthic acid; Phenol trinitrate; Phenoltrinitrate; Picral; Picronitric acid; Pikrinezuur [Dutch]; Pikrinsaeure [German]; Pikrynowy kwas [Polish]; Trinitrophenol; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Explosives
Description
Yellow, odorless solid. [Note: Usually used as an aqueous solution.]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as an explosive, dye, fungicide, copper etching agent, and chemical intermediate for metal picrates; it is used in the manufacturing of leather products, batteries, colored glass, textile mordants, rocket fuel, and photographic emulsions; [HSDB]
Comments
Workers may develop skin sensitization. Laboratory dogs receiving subcutaneously 100-125 mg/kg die of respiratory paralysis and have liver abnormalities on pathological examination. [HSDB] Irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; May stain yellow the hair and skin; [ICSC] Danger of skin sensitization; [MAK]
Restricted
An OSHA Class A Explosive (1910.109)
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
0.1 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
0.1 mg/m3
IDLH (NIOSH)
75 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: The ingestion of 1 to 2 grams of picric acid has been reported to cause severe poisoning [ACGIH 1991]. [Note: An oral dose of 1 to 2 grams is equivalent to a worker being exposed to 660 to 1,330 mg/m3 for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Vapor Pressure
7.5E-07 mm Hg
Explanatory Notes
VP from HSDB;
Reference Link #2
NFPA
burn readily
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Nephrotoxin
Yes
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: