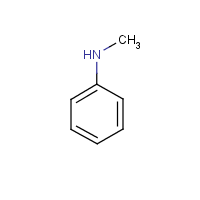
Monomethyl aniline
Agent Name
Monomethyl aniline
CAS Number
100-61-8
Formula
C7-H9-N
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
(Methylamino)benzene; Aniline, N-methyl-; Benzeneamine, N-methyl-; Methylphenylamine; Monomethylaniline; N-Methylaminobenzene; N-Methylbenzenamine; N-Methylphenylamine; N-Monomethylaniline; N-Phenylmethylamine; [ChemIDplus] UN2294
Category
Amines, Aromatic
Description
Yellow to light-brown liquid with a weak, ammonia-like odor; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a solvent and in organic synthesis; [ACGIH] Solvent for organic reactions and for nitrocellulose; [HSDB]
Comments
Methemoglobinemia and liver injury occur in animals exposed to high concentrations over a period of weeks and months. There are no reports of human poisoning by monomethyl aniline. Listed in table of "Industrial Chemicals for Which Methemoglobin Formation is the Principal Cause of Toxicity"; [ACGIH] Can induce methemoglobinemia; [ICSC]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
BEI
Methemoglobin in blood = 1.5% of hemoglobin during or at end of shift. [ACGIH]
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.5 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
2 ppm
MAK
0.5 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
100 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Other animal data: It has been reported that a dog survived 50 sevenhour exposures to 86 ppm [Treon et al. 1949].
Vapor Pressure
0.453 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
1.6 ppm
Odor Threshold High
2 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Odor threshold from AIHA; Flash point = 175 deg F; VP from HSDB;
Adverse Effects
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is primary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: