Propane
Agent Name
Propane
CAS Number
74-98-6
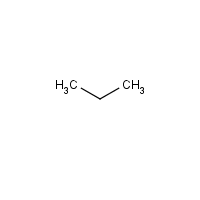
Formula
C3-H8
Major Category
Toxic Gases & Vapors
Synonyms
A-108; Dimethylmethane; HC 290; Hydrocarbon Propellant A-108; LPG; Liquefied petroleum gas; Petroleum gas, liquefied; Propane; Propyl hydride; Propyldihydride; R 290; n-Propane; [ChemIDplus] UN1978
Category
Simple Asphyxiants
Description
Colorless, odorless gas. [Note: A foul-smelling odorant is often added when used for fuel purposes. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas.]; [NIOSH] Vapor density = 1.56 (heavier than air); [HSDB]
Sources/Uses
Used as a fuel, solvent, refrigerant, and propellant; [Hawley]
Comments
Propane is a simple asphyxiant. [LaDou, p. 558] Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH] "Critical Effects" for aliphatic hydrocarbon gases are CNS depression; cardiac sensitization; [ACGIH] Propane is in the list of "Some volatile substances which may be abused by inhalation" published on the web site of the U.N. International Drug Control Programme, indicating its potential to cause narcosis in workers. [Reference #1] Evaporating liquid can cause frostbite; Inhalation of high concentrations can cause CNS depression and cardiac arrhythmias; [ICSC]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
No
PEL (OSHA)
1000 ppm
MAK
1000 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
2100 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
It has been reported that brief inhalation exposures to 10,000 ppm propane cause no symptoms in humans [Braker and Mossman 1980]. Propane is considered to be a simple asphyxiant [ACGIH 1991].
Odor Threshold Low
12225 ppm
Odor Threshold High
20005 ppm
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) > 800,000 ppm/15m
Explanatory Notes
IDLH = 10% LEL; Odor threshold from AIHA; Flash point = -156 deg F; See "Appendix F: Minimal Oxygen Content." A simple asphyxiant and explosion hazard; [TLVs and BEIs]
NFPA
burn readily
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Other Poison
Simple Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: