Sodium fluoroacetate
Agent Name
Sodium fluoroacetate
CAS Number
62-74-8
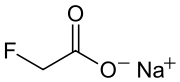
Formula
C2-H3-F-O2.Na
Major Category
Pesticides
Synonyms
SFA; Sodium monofluoroacetate; [NIOSH] Fluoroacetic acid, sodium salt; Fratol; Furatol; Compound 1080; Ratbane 1080; Sodium fluoroacetic acid; 1018; 1080; [ACGIH] UN2629
Category
Rodenticides
Description
Fluffy, colorless to white (sometimes dyed black), odorless powder. [Note: A liquid above 95 degrees F.] [rodenticide] [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used to eliminate coyotes and rodents; [ACGIH]
Comments
A metabolic poison that combines with acetyl coenzyme A, causing the formation of fluorocitrate, which disrupts the Krebs cycle; Symptoms usually begin within 3 hours of ingestion. Patients die from ventricular fibrillation, frequently associated with hypokalemia and hypocalcemia. [Ford, p. 856-7] Very toxic by inhalation of dust, skin absorption, or ingestion; [CHEMINFO] 5 mg/kg is the estimated lethal oral dose for humans. After a lethal dose, death is preceded by seizures and ventricular fibrillation. [ACGIH] Damages the liver and kidneys in poisoning cases; [Merck Index] Poisoning cases may resemble those caused by other cellular toxins (hydrogen cyanide and hydrogen sulfide), but onset of symptoms is usually slower for fluoroacetate; [Olson, p. 242]
Restricted
Use restricted in the US to livestock collars to protect sheep and cattle from coyotes; Used to control vertebrates in Australia and New Zealand; [Olson, p. 242]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Yes
TLV (ACGIH)
0.05 mg/m3
PEL (OSHA)
0.05 mg/m3
MAK
0.05 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
IDLH (NIOSH)
2.5 mg/m3
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: The probable oral lethal dose has been reported to be 50 mg [Deichmann and Gerarde 1969]. [Note: An oral dose of 50 mg is equivalent to a worker being exposed to about 30 mg/m3 for 30 minutes, assuming a breathing rate of 50 liters per minute and 100% absorption.]
Explanatory Notes
A non-combustible solid; Vapor pressure is approximately zero.[CHEMINFO]
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: