N,N'-Diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine
Agent Name
N,N'-Diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine
CAS Number
74-31-7
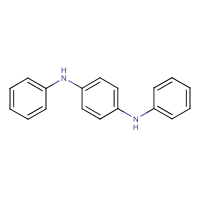
Formula
C18-H16-N2
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
N,N'-Diphenyl-4-phenylenediamine; p-Phenylenediamine, N,N'-diphenyl-; 1,4-Benzenediamine, N,N'-diphenyl-; 1,4-Bis(phenylamino)benzene; 1,4-Dianilinobenzene; 4,4'-Diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine; 4-Phenylaminodiphenylamine; AgeRite DPPD; Altofane DIP; Antage DP; Antigene P; Antioxidant H; DFFD; DPPD; Diafen FF; Diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine; Ekaland DPPD; Flexamine G; JZF; N,N'-Difenyl-p-fenylendiamin [Czech]; N,N'-Diphenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine; N,N-Diphenyl-1,4-benzenediamine; Naugard J; Nocrac DP; Nonflex H; Nonox DPPD; Permanax 18; Permanax DPPD; Stabilizer DPPD; p-Bis(phenylamino)benzene; p-Phenylaminodiphenylamine; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Amines, Polyaromatic
Description
Colorless solid; Commercial product is greenish-brown solid; [Merck Index] Colorless, grey, or white solid; [HSDB] Powder; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used as antioxidant (rubber, polyethylene, feedstuffs, petroleum, vegetable oils, animal fats, and oils), polymerization inhibitor, copper degradation inhibitor, and as an intermediate (dyes, drugs, plastics, and detergents); [HSDB]
Comments
May cause skin sensitization; [ICSC] Danger of skin sensitization; [MAK] Food concentrations as low as 0.005% increase frequency of stillbirths in pregnant rats; Emergency treatment: "Paraphenylenediamine"; In sensitized individuals, paraphenylenediamine may cause allergic contact dermatitis following application as a hair dye and asthma following inhalation; Following ingestion, can cause angioneurotic edema, methemoglobinemia, acute tubular necrosis, and hepatotoxicity; An adult died after ingestion of 3 grams of p-phenylenediamine; Another adult who ingested 1800 mg developed angioneurotic edema and acute renal failure; [HSDB] May cause skin sensitization; [eChemPortal: ESIS] A mild eye irritant; Causes changes in liver weight, renal tubules, and clotting factors in repeated feeding studies of rats; [RTECS] See "p-Phenylenediamine."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
6.35E-09 mm Hg
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Methemoglobinemia
MetHgb is secondary toxic effect
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent:
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: