Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid
Agent Name
Perfluorooctane sulfonic acid
Alternative Name
PFOS
CAS Number
1763-23-1
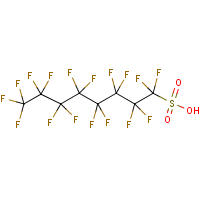
Formula
C8-H-F17-O3-S
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
PFOS; 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-Heptadecafluoro-1-octanesulfonic acid; 1-Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid; EF 101; Eftop EF 101; Heptadecafluoro-1-octanesulfonic acid; Heptadecafluorooctane-1-sulphonic acid; PFOS; Perfluorooctane sulfonate; Perfluorooctylsulfonic acid; 1-Octanesulfonic acid, 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptadecafluoro-; [ChemIDplus]
Category
Perfluoroalkyl Acids
Description
Liquid; [HSDB] Off-white to grey liquid; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used as a surfactant in fire-fighting foams, alkaline cleaners, floor polishes, metal plating baths, and etching acids for circuit boards; Also used as an acid catalyst for photoresists and the active ingredient for ant bait traps; [HSDB] PFOS and its precursors used as protective surface coatings (i.e. carpets, fabrics, and food packaging) and in specialty chemicals (i.e. fire-fighting foams, hydraulic fluids, mining and oil-well surfactants, and consumer products); [Reference #2] "The manufacturing of PFOS began in the United States in 1948. In 2000, the major manufacturer, 3M Corporation, announced that it would stop making many of its well-known Scotchgard stain-repellent products after finding the PFOS persists in the environment and is found widely in numerous species, including humans." [PMID 21346631]
Comments
Animals given high doses develop liver enlargement and elevated cholesterol. "The presence of PFOS in nonoccupationally exposed populations and wildlife has raised concerns about the environmental and health effects of PFOS and prompted the phase-out of the production of POSF-based chemicals by the major producer." A study of 1895 employees in PFOS-exposed jobs, no increased risks for several cancers, low birth weights, or other common health problems were found. [Reference #1] Caused severe eye irritation in rabbits in one study, and mild to moderate irritation in several others; Histopathological changes to the liver observed in two year feeding study with rats with doses as low as 0.06-0.23 (males) and 0.007-0.21 (females) mg/kg body weight; Increased frequency of hepatocellular adenomas seen in chronic animal studies at the highest doses (greater than doses which caused non-neoplastic effects); No evidence of mutagenicity in various in vitro and in vivo assays; Teratogenic effects (incomplete skull closure) observed at doses below maternal NOEL in rats; Effects in a multi-generational study with rats (F1 generation) include significant reductions in litter sizes, viability and lactation indices, and slower development pups; [Reference #2] Corrosive to skin and eyes; A respiratory tract irritant; Can be absorbed through skin; "Animal studies conducted on organic fluorochemicals which are present in this product indicate effects including liver disturbances, weight loss, loss of appetite, lethargy, and neurological, pancreatic, adrenal and hematologic effects. There are no known human health effects from anticipated exposure to these organic fluorochemicals when used as intended and instructed." [MSDSonline: 3M MSDS] "Serum PFAS concentrations were not associated with increased cardiometabolic risk measures in this population of firefighters." [PMID 33105404]
Restricted
3M to phase out perfluorooctane sulfonates (PFOs) by 2001; [HSDB] "PFOS use in new AFFFs [aqueous film-forming foams] and other products were banned in the European Union in 2011 and Canada in 2013." [PMID 31045850]
Reference Link #1
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
MAK
0.01 mg/m3, inhalable fraction
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 5,200 mg/m3
Reference Link #2
Adverse Effects
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: