Trifluorobromomethane
Agent Name
Trifluorobromomethane
Alternative Name
Bromotrifluoromethane
CAS Number
75-63-8
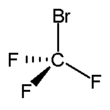
Formula
C-Br-F3
Major Category
Solvents
Synonyms
Bromofluoroform; Bromotrifluoromethane; Carbon monobromide trifluoride; Daiflon 13B1; F 13B1; F-13B1; FC 13B1; FE 1301; Flugex 13B1; Fluorocarbon 1301; Freon 13B1; Halocarbon 13B1; Halon 1301; Khladon 13B1; Monobromotrifluoromethane; R 13B1; Refrigerant 13B1; Trifluorobromomethane; Trifluoromethyl bromide; Trifluoromonobromomethane; [ChemIDplus] UN1009
Category
Chlorofluorocarbons
Description
Colorless, odorless gas. [Note: Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas.]; [NIOSH]
Sources/Uses
Used as a fire extinguisher and chemical intermediate; [ACGIH]
Comments
Slightly increased reaction times were recorded in volunteers exposed to 4% trifluorobromomethane for 3 minutes. [ACGIH] Possible frostbite from contact with liquid; [NIOSH] An eye irritant; Evaporating liquid can cause frostbite; Inhalation of high concentrations can cause CNS depression; [ICSC] See "CHLOROFLUOROCARBONS."
Restricted
See CHLOROFLUOROCARBONS
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Skin Designation (ACGIH)
Insufficient data
TLV (ACGIH)
1000 ppm
PEL (OSHA)
1000 ppm
MAK
1000 ppm
IDLH (NIOSH)
40000 ppm
Excerpts from Documentation for IDLHs
Human data: Volunteers exposed to 70,000 ppm for 3 minutes experienced lightheadedness and disturbances in balance and ability to respond to visual stimulus [Reinhardt and Reinke 1972]; 3 hours to 70,000 ppm caused decrements in mental performance tests [Harrison et al. 1982]. Exposure to 50,000 ppm for 20 to 25 minutes caused drowsiness, lightheadedness, and a slight effect on judgment [Hine et al. 1968]. Three volunteers experienced mild nose and throat discomfort after 28 minutes of exposure to 71,000 ppm [Stewart et al. 1978]. Others reported that a 30minute exposure at 43,000 to 45,000 ppm caused dizziness, lightheadedness, euphoria, and disturbances in equilibrium and coordination [Stewart et al. 1978].
Lethal Concentration
LC50 (rat) = 84,000 ppm/15 min
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Acute solvent syndrome
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Other Poison
Simple Asphyxiant
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: