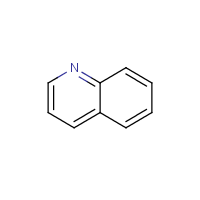
Quinoline
Agent Name
Quinoline
CAS Number
91-22-5
Formula
C9-H7-N
Major Category
Nitrogen Compounds
Synonyms
1-Azanaphthalene; 1-Benzazine; 2,3-Benzopyridine; B 500; B-500; Benzo(b)pyridine; Benzopyridine; Benzopyridine (VAN); Chinoleine; Chinolin [Czech]; Chinoline; Leucol; Leukol; Quinolin; [ChemIDplus] UN2656
Category
Quinolines
Description
Colorless hygroscopic liquid with characteristic odor; Turns brown after exposure to light; [ICSC] Clear liquid that darkens as ages; [Hawley] Light yellow liquid; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used to make paints, dyes, and other chemicals; Also used as a preservative for anatomical specimens, solvent for resins and terpenes, fungistat, corrosion inhibitor, antimalarial drug, flavoring agent, and decarboxylation reagent; [HSDB] Extracted from coal-tar distillates; occurs in polluted air and cigarette smoke; [AIHA]
Comments
A skin and eye irritant; May have effects on the liver and retina; Possibly carcinogenic in humans; [ICSC] Causes lethargy, respiratory depression, and coma in high-dose animal experiments; No rats died when exposed to saturated vapor (about 78 ppm) for 8 hours, but all rats died within 6 hours after exposure to 4000 ppm; [HSDB] An irritant; May cause serious injury to eyes; Can be absorbed through skin; [MSDSonline]
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
Vapor Pressure
0.06 mm Hg
Odor Threshold Low
71 ppm
Explanatory Notes
Flash point = 105 deg C; [ICSC] Odor threshold from HSDB; VP from ChemIDplus;
NFPA
high ambient temp required
WEEL
0.001 ppm
Adverse Effects
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
IARC Carcinogen
Possible (2b)
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Processes
Industrial Processes with risk of exposure: