Selenious acid
Agent Name
Selenious acid
CAS Number
7783-00-8
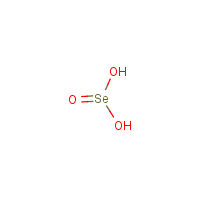
Formula
H2-O3-Se
Major Category
Other Classes
Synonyms
Hydrogen selenite; Monohydrated selenium dioxide; Selenite; [ChemIDplus] UN3283
Category
Other Inorganic Compounds
Description
Deliquescent solid; [Merck Index] Colorless or white hygroscopic solid; [HSDB] Colorless or white odorless crystalline solid; [MSDSonline]
Sources/Uses
Used as a reagent for alkaloids, an oxidizing agent, and a medication; A gun-blueing agent (Super Blue or Gun Blue) contains 4% selenious acid and 2.5% cupric sulfate in hydrochloric acid; [HSDB]
Comments
A corrosive substance that can cause injury to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; Inhalation may cause pulmonary edema; May cause skin sensitization; May cause impairment of the CNS and liver; [ICSC] Can cause irritation and burns to skin; After a suicidal ingestion of Gun Blue, the patient had pulmonary edema and acute tubular necrosis; Selenium levels in tissues were 9-90 times normal; In another poisoning case, a 2 year old girl ingested about 11 mL of gun blueing agent; Plasma selenium levels were 20 times normal 5 hours after ingestion, but she survived; [HSDB]; A corrosive substance that can cause injury to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract; Inhalation may cause chemical pneumonitis; [MSDSonline] See "Selenium."
Biomedical References
Exposure Assessment
TLV (ACGIH)
0.2 mg/m3, as Se
PEL (OSHA)
0.2 mg/m3, as Se
MAK
0.02 mg/m3, as Se, inhalable fraction
IDLH (NIOSH)
1 mg/m3, as Se
Explanatory Notes
VP = 2 mm Hg at 15 deg C; [Merck Index] The Guide in the Emergency Response Guidebook is for "Selenium compound, solid, n.o.s."
Adverse Effects
Skin Sensitizer
Yes
Toxic Pneumonitis
Yes
Neurotoxin
Other CNS neurotoxin
Hepatotoxin
Hepatoxic (a) from occupational exposure (secondary effect) or (b) in animal studies or in humans after ingestion
Reproductive Toxin
Yes
Dermatotoxin
Skin burns
Diseases, Processes, and Activities Linked to This Agent
Diseases
Occupational diseases associated with exposure to this agent: